IBM SAN40B-4 User Guide - Page 53
Testing, fiber, cable
 |
UPC - 883436031479
View all IBM SAN40B-4 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 53 highlights
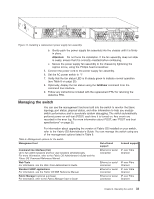
B 1 E A IOIOI ! D scale: 1/8" = 1" C 3 AMmoaTuxTniEmtinNugmTtosIcObreeNw5lm:enmgtohrfo1r3r/a6c4k in. C B24_0005 2 Figure 12. Removing an SFP Item A B C D E 4 Description Switch chassis Cable release SFP Bail Cabled Fibre Channel ports Testing a port, SFP, and fiber cable The PortLoopbackTest command is used to verify the functional operation of the switch by sending frames from the port "N" transmitter and looping them back into the same port "N" receiver. The loopback is done at the parallel loopback path. The path exercised in this test does not include the media or the fiber cable. However if data transmission errors indicate that a port, SFP or cable are faulty, you can use this command to determine whether the port is faulty. You can use those results to isolate the problem to either the port or the SFP and cable combination. If a port is faulty, the switch will need to be replaced. If the port is not faulty, the problem is either with the SFP or the cable. Chapter 3. Operating the switch 29