TP-Link RE350 RE350EU V1 User Guide - Page 41
Specifications, T5. How can I know that my wireless signal has been boosted by extender?
 |
View all TP-Link RE350 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 41 highlights
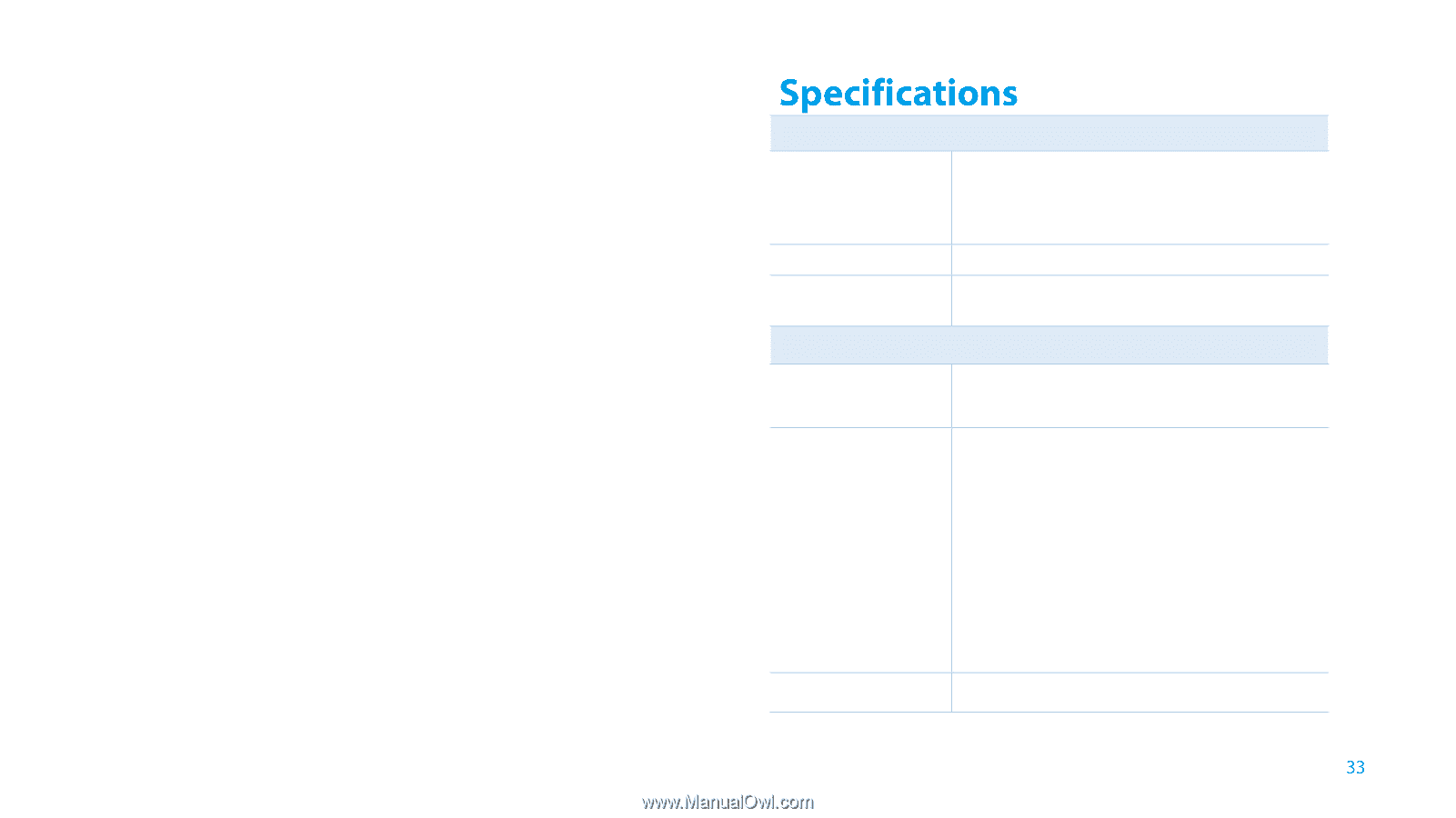
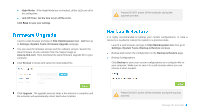
5. Enable the router's MAC filter, wireless access control, or ACL. Now, you have successfully configured your extender. T5. How can I know that my wireless signal has been boosted by extender? An easy way is to compare the signal strength of your target wireless network (symbolized by its SSID), with extender in operation vs. out of operation. Before comparison, you'd better make sure your computer can obtain an IP address from your target wireless network and thus access the Internet, either via extender or without. T6. Will the extender work if I connect its ETHERNET port to the router via Ethernet cable? Sorry, it won't work. The extender is designed to connect wirelessly to the router, while the ETHERNET port is designed to connect with a wired device, like Internet TV, Gaming console, DVR and so on. T7. Why does the wireless transmission rate speed down, while the wireless signal is stronger after repeated by extender? In compliance with the wireless transmission protocol, all the extender devices are set to work in half-duplex instead of full-duplex mode. In other words, the extender has to process one-way communication between your root Wireless router (or AP) and the terminal clients; so the transmission time will be double-increased, while the speed will be decreased. TP-LINK recommends that you connect to the extender when your home network connection is poor, or when you want a larger wireless coverage to eliminate "dead zone". General Standards and Protocols Safety & Emission Ports Wireless Frequency Band Radio Data Rate Security IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.1x, IEEE 802.11e, IEEE 802.11i, IEEE 802.11ac, TCP/IP, DHCP CE One 10/100/1000Mbps Auto-Negotiation LAN RJ45 port 2.4GHz:2.4~2.4835GHz 5GHz:5.15~5.25GHz 2.4GHz: 11n:up to 300Mbps 11g:54/48/36/24/18/12/9/6Mbps 11b:11/5.5/2/1Mbps 5GHz: 11ac: up to 867Mbps 11n: up to 300Mbps 11a: 54/48/36/24/18/12/9/6Mbps WEP, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK Appendix