HP 30b HP 20b Business Consultant and HP 30b Business Professional User's Guid - Page 20
Chain Mode, Algebraic Mode
 |
View all HP 30b manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
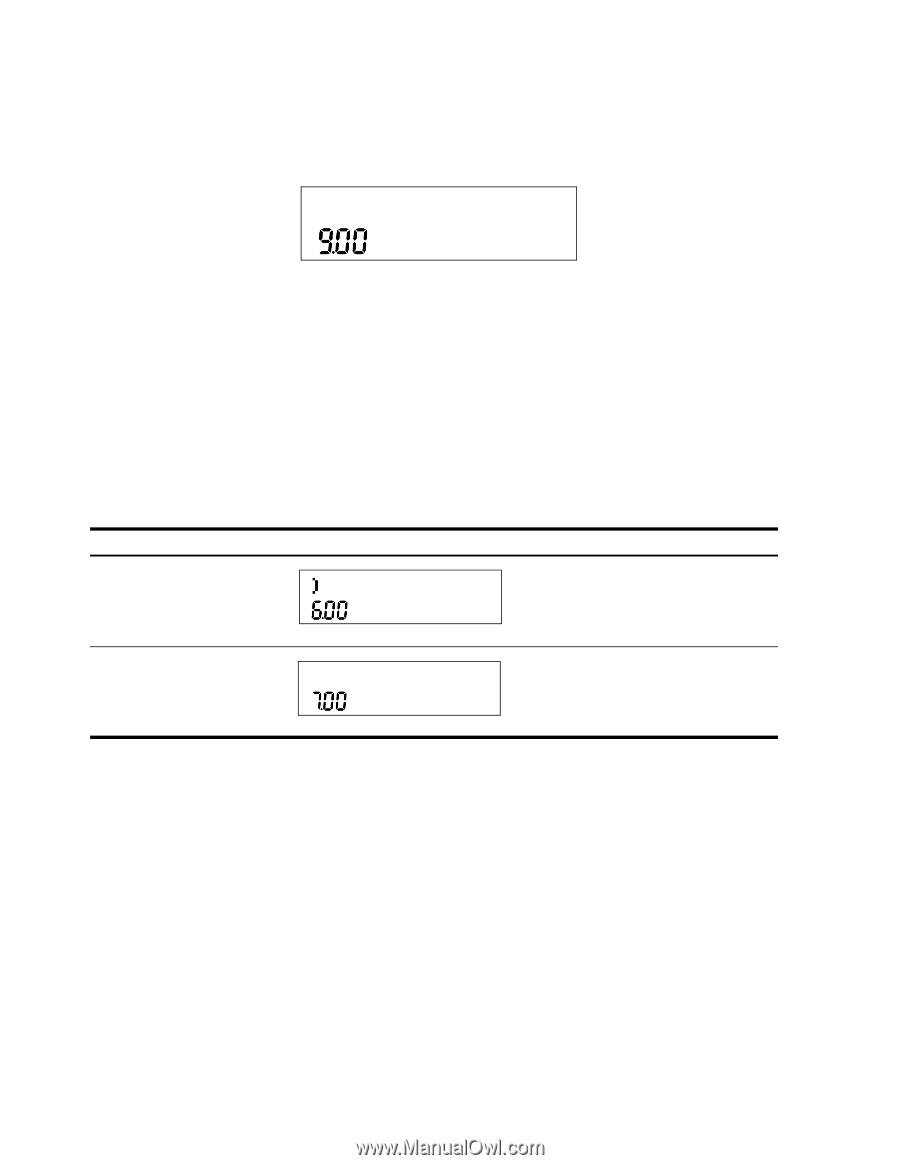
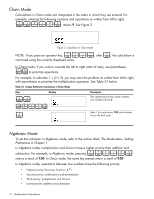
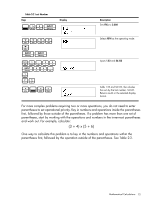
Chain Mode Calculations in Chain mode are interpreted in the order in which they are entered. For example, entering the following numbers and operations as written from left to right, 1+2*3=, returns 9. See Figure 2. Figure 2 Calculation in Chain Mode +-*/ = NOTE: if you press an operator key, , after , the calculation is continued using the currently displayed value. In Chain mode, if you wish to override the left to right order of entry, use parentheses (D to prioritize operations. For example, to calculate 1 + (2 x 3), you may enter the problem as written from left to right, with parentheses to prioritize the multiplication operation. See Table 2-1 below. Table 2-1 Simple Arithmetic Calculations in Chain Mode Keys 1+ Display Description Sets operational priority, inputs numbers, and multiplies 2 and 3. (2*3D = Adds 1 to 6 and returns 7.00 on the bottom line as the final result. Algebraic Mode To set the calculator in Algebraic mode, refer to the section titled, The Mode Menu: Setting Preferences in Chapter 1. In Algebraic mode, multiplication and division have a higher priority than addition and 1+2*3= subtraction. For example, in Algebraic mode, pressing returns a result of 7.00. In Chain mode, the same key presses return a result of 9.00. In Algebraic mode, operations between two numbers have the following priority: • Highest priority: the power function ( y x ) • Second priority: combinations and permutations • Third priority: multiplication and division • Lowest priority: addition and subtraction 12 Mathematical Calculations