HP 30b HP 20b Business Consultant and HP 30b Business Professional User's Guid - Page 74
The Depreciation Menu, the type of depreciation selected. Press
 |
View all HP 30b manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 74 highlights
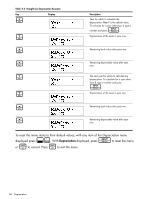
The Depreciation Menu :\ Press to open the Depreciation menu. To select a depreciation method, press I. See Figure 1. Input the values required for the calculation: • Asset life • Starting date or month of the depreciation • Cost and salvage values • Declining balance factor (DecBal and DBXover only) • The first year for which you want to view the depreciation schedule Scroll through the items of the sub-menu for the selected depreciation method by pressing < > or repeatedly. To change the value of the displayed item, key in a number and I press . For the Start item, enter either a number or an actual date, depending on < the type of depreciation selected. Press repeatedly to view the depreciation schedule. < NOTE: pressing on the last item of a sub-menu returns you to the Year item and increments it (see Figure 1). Brief descriptions of the methods used to calculate depreciation are provided in Table 11-1. Table 11-2 describes the items found in the depreciation sub-menus. For an example calculating depreciation using the straight-line method, see Table 11-3. Table 11-1 Depreciation Methods Depreciation Method Sline SOYD DecBal DBXover French SL Amort F Description Straight line is a method of calculating depreciation presuming an asset loses a certain percentage of its value annually at an amount evenly distributed throughout its useful life. Sum-of-the-years' digits is an accelerated depreciation method. In SOYD, the depreciation in year y is (Life-y +1)/SOY of the asset, where SOY is the sum-of-the-years for the asset, or, for an asset with a 5-year life, 5+4+3+2+1=15. Declining balance is an accelerated depreciation method that presumes an asset will lose the majority of its value during the first few years of its useful life. Declining balance crossover is an accelerated depreciation method that presumes an asset will lose the majority of its value in the first few years of its useful life, but that it will revert to a consistent depreciation during the latter part of its life, which is then calculated using the straight line method. Straight line French. This method of depreciation is similar to the Straight line method, except an actual calendar date in mm.dd format is entered in for Start= to indicate when the asset was first placed into service. French amortization. This method is an accelerated depreciation method with a crossover to the French Straight Line method. 66 Depreciation