HP StorageWorks 2/16V HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.X Procedures User Guide (AA- - Page 58
Troubleshooting certificates, Table 11 SSL messages and actions, Configuring SNMP agent and traps
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 2/16V manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 58 highlights
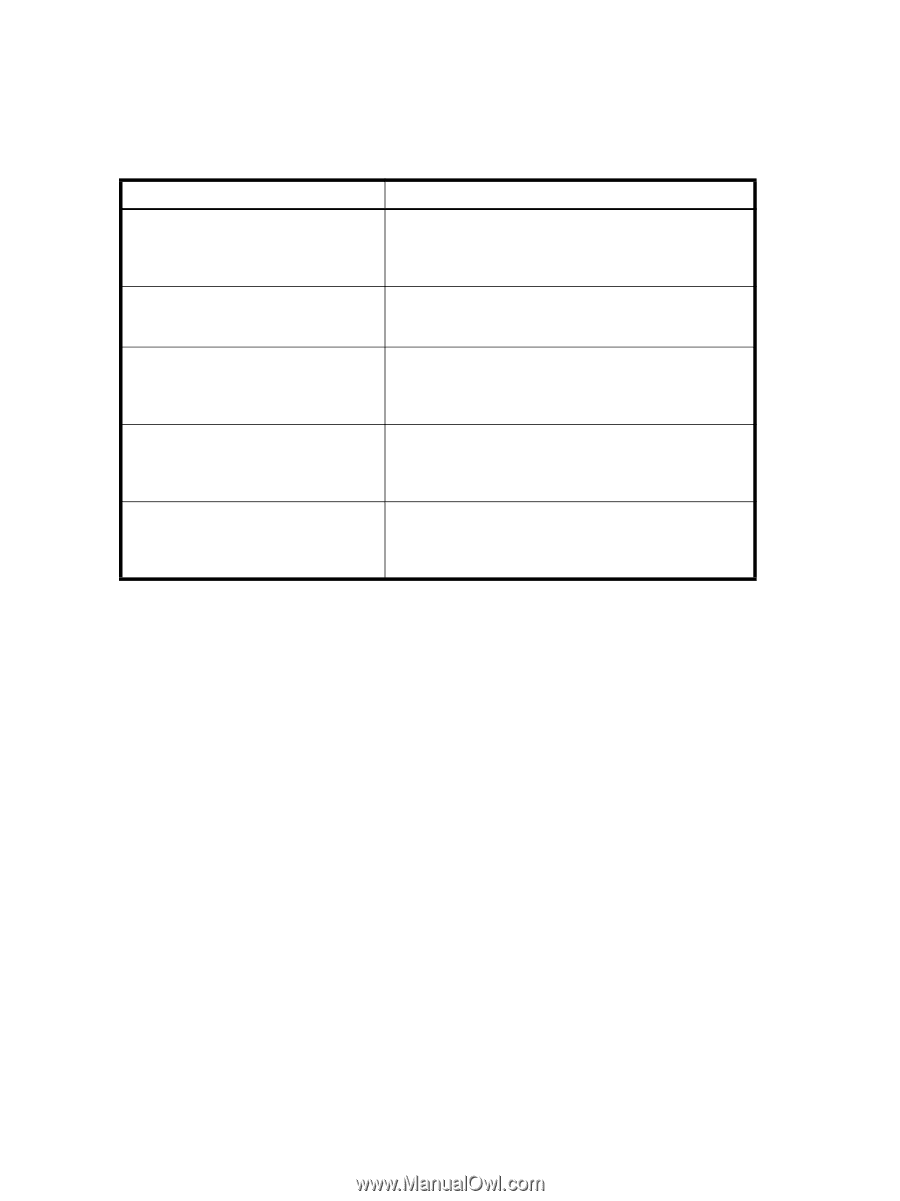
Troubleshooting certificates If you receive messages in the browser or in a pop-up window when logging in to the target switch using HTTPS, see Table 11. Table 11 SSL messages and actions Message Action The page cannot be displayed The security certificate was issued by a company you have not chosen to trust. The SSL certificate is not installed correctly or HTTPS is not enabled correctly. Make sure that the certificate has not expired, that HTTPS is enabled, and that certificate file names are configured correctly. The certificate is not installed in the browser. Install it as described in "Configuring the browser" on page 56. The security certificate has expired or is not yet valid The name on the security certificate is invalid or does not match the name of the site file This page contains both secure and nonsecure items. Do you want to display the nonsecure items? Either the certificate file is corrupted or it needs to be updated. Click View Certificate to verify the certificate content. If it is corrupted or out of date, obtain and install a new certificate. The certificate is not installed correctly in the Java Plug-in. Install it as described in "Installing a root certificate to the Java Plug-in" on page 57. Click No in this pop-up window. The session opens with a closed lock icon on the lower-right corner of the browser, indicating an encrypted connection. Configuring SNMP agent and traps You can perform a configuration for the transmission of SNMP information to management stations. SNMPv3 and SNMPv1 are supported. The configuration process involves configuring the SNMP agent and configuring SNMP traps. The following commands are used in the process: • The configure command sets the security level. You can specify no security, authentication only, or authentication and privacy. • The snmpConfig command configures the SNMP agent and traps for SNMPv3 or SNMPv1 configurations. • If necessary for backward compatibility, you can use these legacy commands for the configuration of SNMP v1: • The agtCfgShow, agtCfgset, and agtCfgDefault commands configure the SNMPv1 agent. • The snmpMibCapSet command filters at the trap level and the snmpMibCapShow command displays the trap filter values. The SNMP trap configuration specifies the MIB trap elements to be used to send information to the SNMP management station. There are two main MIB trap choices: • HP-specific MIB trap is associated with the HP-specific StorageWorks MIB (SW-MIB); it monitors HP StorageWorks switches specifically. • FibreAlliance MIB trap is associated with the FibreAlliance MIB (FA-MIB); it manages SAN switches and devices from any company that complies with FibreAlliance specifications. If you use both SW-MIB and FA-MIB, you might receive duplicate information. You can disable the FA-MIB, but not the SW-MIB. 58 Configuring standard security features