Cisco 7921G Administration Guide - Page 30
Cisco 4100 Series Wireless LAN Controller-For medium to large deployments. Works with Cisco
 |
UPC - 882658123108
View all Cisco 7921G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
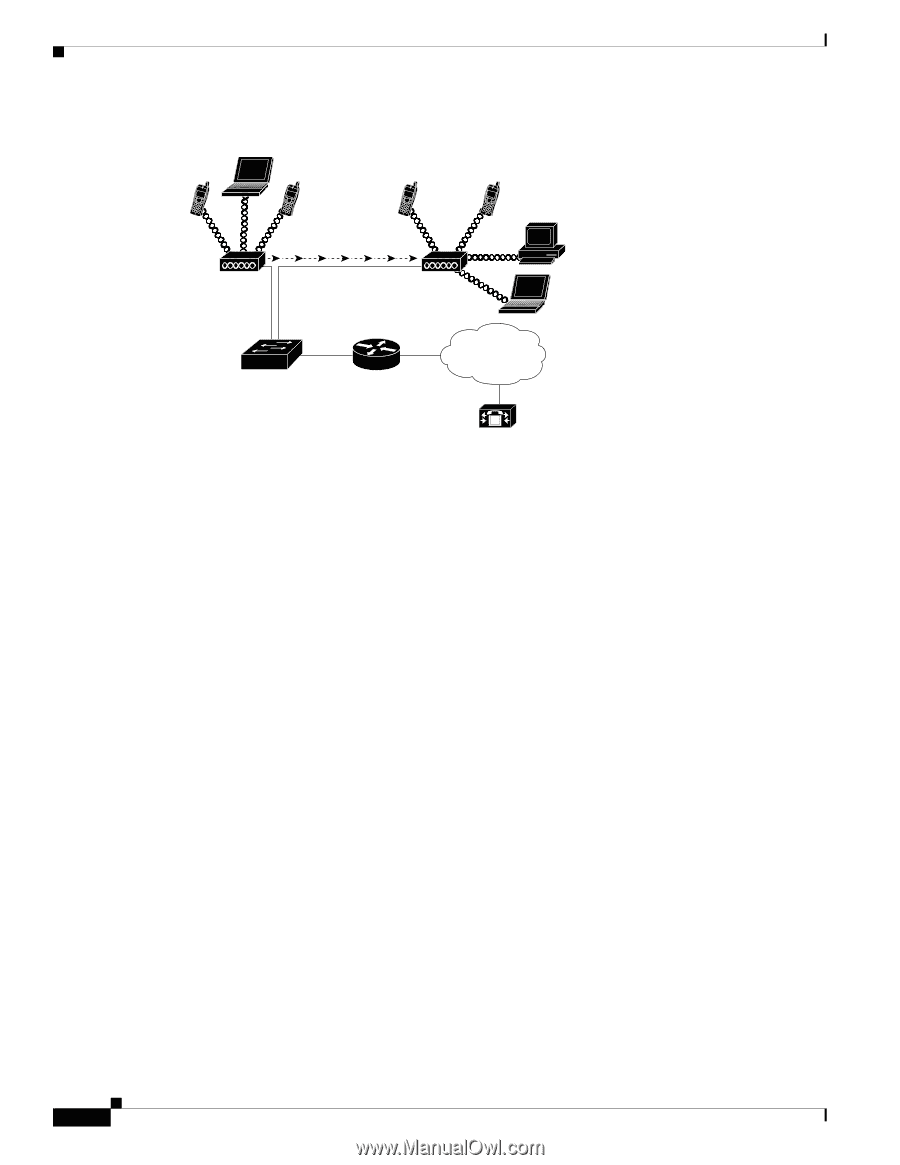
Understanding the Wireless LAN Figure 2-1 WLAN with Wireless IP Phones Chapter 2 Overview of the VoIP Wireless Network 113946 M When a wireless IP phone powers on, it searches for and becomes associated with an AP. As users move from one location to another, the wireless IP phone roams out-of-range of one AP into the range of another AP. The wireless IP phone builds and maintains a list of eligible APs and reconnects to an AP in that list. See Associating to an AP, page 2-10 for more information. The AP uses its connection to the wired network to transmit data and voice packets to and from the switches and routers. Voice signaling is transmitted to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server for call processing and routing. APs are critical components in a WLAN because they provide the wireless links or "hot spots" to the network. Cisco requires that the APs supporting voice communications use Cisco IOS Release 12.3(8)JA or later. Cisco IOS software provides features for managing voice traffic. In some WLANs, each AP has a wired connection to an Ethernet switch, such as a Cisco Catalyst 3750, that is configured on a LAN. The switch provides access to gateways and the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server to support wireless IP telephony. Some networks have wired components that support wireless components. The wired components could consist of switches, routers, and bridges with special modules to enable wireless capability. The Cisco Unified WLAN can have the following components: • Cisco Aironet Series Access Points-802.11a/b/g enterprise-class access points with integrated antennas or antenna connections for easy deployment. • Cisco 2000 Series Wireless LAN Controller-For small to medium sized networks, such as branch offices. Works with Cisco lightweight access points. • Cisco 4100 Series Wireless LAN Controller-For medium to large deployments. Works with Cisco lightweight access points. • Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controller-For large enterprise facilities. The Cisco 4402 and 4404 models support a maximum of 50 and 100 access points respectively. • Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module for Integrated Services Routers-Enables small-to-medium businesses and enterprises to deploy and manage secure WLANs at branch offices. • Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless Services Module (WiSM)-Provides security, mobility, redundancy, and ease of use for WLAN administrators. Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7921G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 7.0 2-2 OL-15985-01