Cisco 7921G Administration Guide - Page 31
Understanding WLAN Standards and Technologies, 802.11 Standards for WLAN Communications - rated
 |
UPC - 882658123108
View all Cisco 7921G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
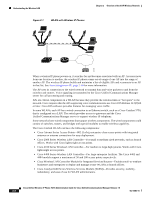
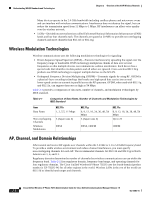
Chapter 2 Overview of the VoIP Wireless Network Understanding WLAN Standards and Technologies • Cisco Catalyst 3750 Series Integrated Wireless LAN Controllers-Adds wireless LAN controller functions to the stackable Cisco Catalyst 3750G Series Switches to improve operating efficiency, security, mobility, and ease of use for WLAN administrators. • Wireless Control System (WCS)-Provides a powerful systems management. System administrators can design, control, and monitor enterprise WLANs from a centralized location. • Cisco 2700 Series Wireless Location Appliance-802.11 based location tracking solution for asset tracking, IT management, and location based security. An open API is included. • Cisco Wireless LAN Client Adapters-Available in CardBus, PCMCIA and PCI form factors, Cisco Aironet Wireless LAN Client Adapters connect desktop and mobile computing devices to the WLAN in 802.11b-compliant or 802.11a-compliant network. For more information about Cisco Unified Wireless Networks, refer to http://wwwin.cisco.com/marketing/mobility/solutions/unified/index.shtml. For more information about the Cisco wireless products, refer to http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/index.html. Understanding WLAN Standards and Technologies This section describes the following concepts: • 802.11 Standards for WLAN Communications, page 2-3 • Radio Frequency Ranges, page 2-3 • Wireless Modulation Technologies, page 2-4 • AP, Channel, and Domain Relationships, page 2-4 • WLANs and Roaming, page 2-6 802.11 Standards for WLAN Communications Wireless LANs must follow the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11 standards that define the protocols that govern all Ethernet-based wireless traffic. The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7921G supports the following standards: • 802.11b-Specifies the radio frequency (RF) of 2.4 GHz for both transmitting and receiving data. Commonly called the Wi-Fi standard. • 802.11g-Uses the same unlicensed 2.4 GHz band as 802.11b, but extends the data rates to provide greater performance by using Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) technology. OFDM is a physical-layer encoding technology for transmitting signals by using RF. • 802.11a-Uses the 5 GHz band that provides more channels and improved data rates by using OFDM technology. Radio Frequency Ranges WLAN communications use the following RF ranges: • 2.4 GHz-Does not require licensing. To reduce interference within this bandwidth, WLANs transmit on non-overlapping channels, which are typically limited to three channels, although Japan uses four channels. OL-15985-01 Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7921G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 7.0 2-3