Cisco CISCO1401 Software Guide - Page 75
Configuring NTP Access Restrictions, no ntp broadcast
 |
UPC - 746320202785
View all Cisco CISCO1401 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 75 highlights
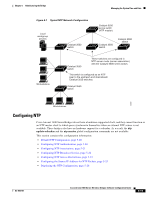
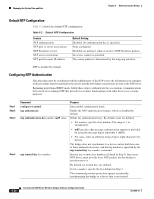
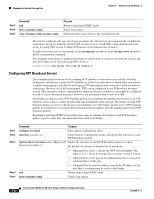
Chapter 5 Administering the Bridge Managing the System Time and Date Step 6 Step 7 Command copy running-config startup-config Purpose (Optional) Save your entries in the configuration file. Configure the connected peers to receive NTP broadcast packets as described in the next procedure. To disable the interface from sending NTP broadcast packets, use the no ntp broadcast interface configuration command. This example shows how to configure an interface to send NTP version 2 packets: bridge(config)# interface gigabitethernet0/1 bridge(config-if)# ntp broadcast version 2 Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to configure the bridge to receive NTP broadcast packets from connected peers: Step 1 Step 2 Command configure terminal interface interface-id Step 3 ntp broadcast client Step 4 exit Step 5 ntp broadcastdelay microseconds Step 6 Step 7 Step 8 end show running-config copy running-config startup-config Purpose Enter global configuration mode. Enter interface configuration mode, and specify the interface to receive NTP broadcast packets. Enable the interface to receive NTP broadcast packets. By default, no interfaces receive NTP broadcast packets. Return to global configuration mode. (Optional) Change the estimated round-trip delay between the bridge and the NTP broadcast server. The default is 3000 microseconds; the range is 1 to 999999. Return to privileged EXEC mode. Verify your entries. (Optional) Save your entries in the configuration file. To disable an interface from receiving NTP broadcast packets, use the no ntp broadcast client interface configuration command. To change the estimated round-trip delay to the default, use the no ntp broadcastdelay global configuration command. This example shows how to configure an interface to receive NTP broadcast packets: bridge(config)# interface gigabitethernet0/1 bridge(config-if)# ntp broadcast client Configuring NTP Access Restrictions You can control NTP access on two levels as described in these sections: • Creating an Access Group and Assigning a Basic IP Access List, page 5-24 • Disabling NTP Services on a Specific Interface, page 5-25 OL-4059-01 Cisco Aironet 1400 Series Wireless Bridges Software Configuration Guide 5-23