Dell PowerConnect Brocade M6505 Brocade 7.1.0 Access Gateway Administrator's G - Page 29
Access Gateway port types, Comparison of Access Gateway ports to standard switch ports
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect Brocade M6505 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
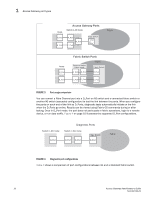
Access Gateway port types 1 • Authentication is not supported between an AG switch running Fabric OS v7.1.0 or later and a fabric running Fabric OS earlier than v7.1.0. If the AG switch is connected to fabric switch running Fabric OS earlier than v7.1.0, the AG switch N_Ports will disable if authentication is enabled on both switches. Devices mapped to N_Ports connected to fabrics operating with Fabric OS before v7.1.0 will also disable. • If authentication is disabled on the Fabric Switch, the AG switch N_Port will come online without authentication policy. • Device and switch policies must be disabled on the AG before converting the switch to Native mode. • Device and switch policies must be disabled on the switch in Native mode before converting it to AG mode. • Authentication policy is disabled by default on all ports in AG mode. • High availability (HA) reboots are supported. Access Gateway port types Access Gateway differs from a typical fabric switch because it is not a switch; instead, it is a mode that you enable on a switch using the ag command. After a switch is set in Access Gateway mode, it can connect to the fabric using node ports (N_Ports). Typically, fabric switches connect to the Enterprise fabric using interswitch link (ISL) ports, such as E_Ports. AG uses the following Fibre Channel (FC) ports: • F_Port - Fabric port that connects a host, HBA, or storage device to a switch in AG mode. • N_Port - Node port that connects a switch in AG mode to the F_Port of the fabric switch. • D_Port - Port configured in diagnostic mode so that various tests can run between it and connected D_Port on another switch across a link. NOTE Initiate the portcfgpersisentenable command on all external or outward facing ports to ensure that these ports come back online after a switch reboot or power failure. For an embedded switch, execute this command through the chassis management console and not the switch CLI or the command may not persist. Refer to "Persisting port online state" on page 31 for more information. Comparison of Access Gateway ports to standard switch ports Access Gateway multiplexes host connections to the fabric. It presents an F_Port to the host and an N_Port to an Edge fabric switch. Using N_Port ID Virtualization (NPIV), AG allows multiple FC initiators to access the SAN on the same physical port. This reduces the hardware requirements and management overhead of hosts to the SAN connections. A fabric switch presents F_Ports (or FL_Ports) and storage devices to the host and presents E_Ports, VE_Ports, or EX_Ports to other switches in the fabric. A fabric switch consumes SAN resources, such as domain IDs, and participates in fabric management and zoning distribution. A fabric switch requires more physical ports than AG to connect the same number of hosts. Figure 3 shows a comparison of the types of ports a switch in AG mode uses to the type of ports that a switch uses in standard mode. Access Gateway Administrator's Guide 9 53-1002743-01