Dell PowerConnect Brocade M6505 Brocade 7.1.0 Access Gateway Administrator's G - Page 71
Failover configurations in Access Gateway, Failover example, An N_Port goes offline.
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect Brocade M6505 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 71 highlights
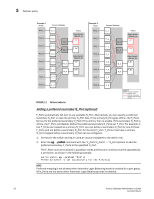
Failover policy 3 Failover configurations in Access Gateway The following sequence describes how a failover event occurs: • An N_Port goes offline. • All F_Ports mapped to that N_Port are temporarily disabled. • If the Failover policy is enabled on an offline N_Port, the F_Ports mapped to it will be distributed among available online N_Ports. If a secondary N_Port is defined for any of these F_Ports, these F_Ports will be mapped to those N_Ports. If the Port Grouping policy is enabled, then the F_Ports only fail over to N_Ports that belong to the same port group as the originally offline N_Port. Failover example The following example shows the failover sequence of events in a scenario where two fabric ports go offline, one after the other. Note that this example assumes that no preferred secondary N_Port is set for any of the F_Ports. • First, the Edge switch F_A1 port goes offline, as shown in Figure 11 on page 52 Example 1 (left), causing the corresponding Access Gateway N_1 port to be disabled. The ports mapped to N_1 fail over; F_1 fails over to N_2 and F_2 fails over to N_3. • Next, the F_A2 port goes offline, as shown in Figure 11 on page 52 Example 2 (right), causing the corresponding Access Gateway N_2 port to be disabled. The ports mapped to N_2 (F_1, F_3, and F_4) fail over to N_3 and N_4. Note that the F_Ports are evenly distributed to the remaining online N_Ports and that the F_2 port did not participate in the failover event. Access Gateway Administrator's Guide 51 53-1002743-01