Dell PowerConnect FCS624S Web Management Interface User Guide - Page 134
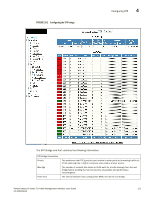
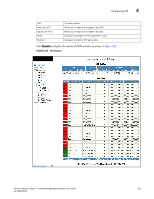
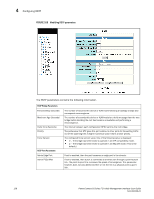
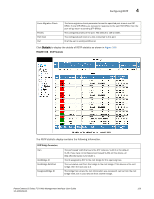
Configuring STP, The STP statistic display contains the following information., STP Bridge Parameters
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect FCS624S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 134 highlights
4 Configuring STP The STP statistic display contains the following information. STP Bridge Parameters Root ID Root Cost Root Port Priority Max.Age Hello Time Hold Time Fwd Delay Topology Last Change Topology Change Counter Bridge Address STP Port Parameters The ID assigned by STP to the root bridge for this spanning tree. The cumulative cost from this bridge to the root bridge. If this device is the root bridge, then the root cost is 0. The port on this device that connects to the root bridge. If this device is the root bridge, then the value is "Root" instead of a port number. A parameter used to identify the root bridge in a spanning tree (instance of STP). The bridge with the lowest value has the highest priority and is the root. The number of seconds this device or VLAN waits for a hello message from the root bridge before deciding the root has become unavailable and performing a reconvergence. The interval between each configuration BPDU sent by the root bridge. The minimum number of seconds that must elapse between transmissions of consecutive Configuration BPDUs on a port. The number of seconds this device or VLAN waits following a topology change and consequent reconvergence. The number of seconds since the last time a topology change occurred. The number of times the topology has changed since this device was reloaded. The STP address of this device or VLAN. Port Priority Path Cost State Forward Transition The port number. The preference that STP gives this port relative to other ports for forwarding traffic out of the spanning tree. A higher numerical value means a lower priority. The port's STP path cost. The port's STP state. The state can be one of the following: • BLOCKING - STP has blocked Layer 2 traffic on this port to prevent a loop. The device or VLAN can reach the root bridge using another port, whose state is FORWARDING. When a port is in this state, the port does not transmit or receive user frames, but the port does continue to receive STP BPDUs. • DISABLED - The port is not participating in STP. This can occur when the port is disconnected or STP is disabled on the port. • FORWARDING - STP is allowing the port to send and receive frames. • LISTENING - STP is responding to a topology change and this port is listening for a BPDU from neighboring bridges in order to determine the new topology. No user frames are transmitted or received during this state. • LEARNING - The port has passed through the LISTENING state and will change to the BLOCKING or FORWARDING state, depending on the results of STP's reconvergence. The port does not transmit or receive user frames during this state. However, the device can learn the MAC addresses of frames that the port receives during this state and make corresponding entries in the MAC table. The number of times STP has changed the state of this port between BLOCKING and FORWARDING. 124 PowerConnect B-Series FCX Web Management Interface User Guide 53-1002268-01