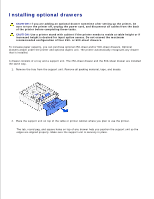
Dell W5300n Dell™ Workgroup Laser Printer W5300 User's Guide - Page 23
Use BOOTP, Use dynamic RARP server and telnet, Parameter, Description
 |
View all Dell W5300n manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
You can also assign an IP address using: BOOTP, or a RARP server and telnet, or static ARP entry and telnet. Use BOOTP BOOTP (Bootstrap Protocol) is an internet standard protocol that lets users on a local area network find their IP address. The BOOTP server, or a forwarding agent, must be attached to the same IP subnet as the new printer. The BOOTP method works like this: First, the printer broadcasts its presence on the network. The BOOTP server hears the broadcast and recognizes the printer hardware address. The BOOTP server replies, setting the IP address, netmask, and gateway in the printer. To set the IP parameters using BOOTP: 1. Determine the hardware address of the printer. This is a 12-digit alphanumeric listed as UAA on the network setup page. Use the number in the right column. 2. Configure the BOOTP server. Edit the BOOTP configuration file (normally /etc/bootptab). This file is a collection of entries for each BOOTP client served by this server. An entry for a particular hardware address sets various IP parameters. The following is an example of a typical entry: net_printer:\ ht=ether:\ ha=000400123ABC:\ ip=192.168.2.0:\ sm=255.255.255.128:\ gw=192.168.0.0:\ hn: Parameter net_printer= ht=ether ha=00400123ABC ip=192.168.2.0 sm=255.255.255.0 gw=192.168.0.0 Description Host name Hardware type (Ethernet) Hardware address IP address Netmask Gateway 3. Make sure BOOTP is enabled. Check the network setup page. 4. Set up the printer host name in the computer. To do so, define the printer IP name and address in the /etc/hosts file or on the name server. This address must match the IP address. You may want to use a host name that is meaningful in your environment (for example, a name that identifies the printer location). Use dynamic RARP server and telnet