Dell XPS /Dimension Gen 5 Owner's Manual - Page 19
RAID Level 0 Configuration
 |
View all Dell XPS /Dimension Gen 5 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
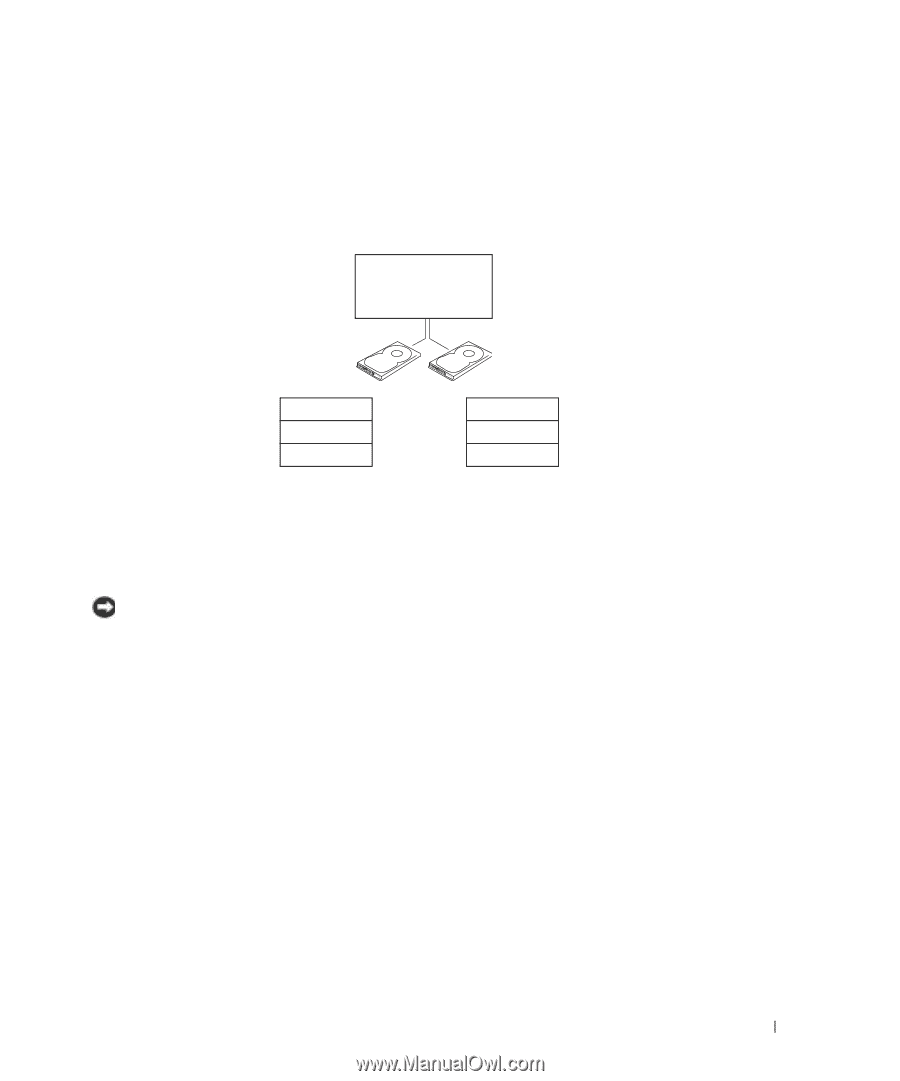
RAID Level 0 Configuration A RAID level 0 configuration uses a storage technique known as "data striping" to provide a high data access rate. Data striping is a method of writing consecutive segments, or stripes, of data sequentially across the physical drives to create a large virtual drive. Data striping allows one of the drives to read data while the other drive is searching for and reading the next block. serial ATA RAID configured for RAID level 0 segment 1 segment 3 segment 5 hard drive 1 segment 2 segment 4 segment 6 hard drive 2 Another advantage of a RAID level 0 configuration is that it utilizes the full capacities of the drives. For example, if you have two 120-GB drives installed, you have 240 GB on which to store data. NOTICE: Because RAID level 0 configurations provide no data redundancy, if one drive fails, then the data on the other drive is also inaccessible. Therefore, ensure that you perform regular backups when you use a RAID level 0 configuration. RAID Level 1 Configuration RAID level 1 uses a data-redundancy storage technique known as "mirroring." When data is written to the primary drive, it is then duplicated, or mirrored, on the other drive. A RAID level 1 configuration sacrifices high data-access rates for its data redundancy advantages. Setting Up and Using Your Computer 19