HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Installation and Getting Star - Page 46
Cabling and Technology Information, Cabling specifications
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
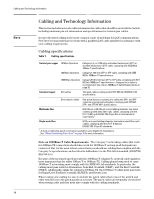
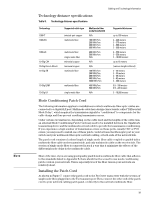
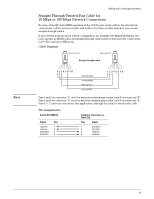
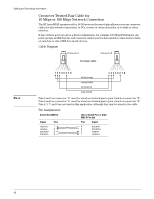
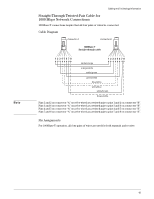
Cabling and Technology Information Note 38 Cabling and Technology Information This section includes network cable information for cables that should be used with the Switch, including minimum pin-out information and specifications for twisted-pair cables. Incorrectly wired cabling is the most common cause of problems for LAN communications. ProCurve recommends that you work with a qualified LAN cable installer for assistance with your cabling requirements. Cabling specifications Table 7. Cabling specifications Twisted-pair copper 10 Mbps Operation Category 3, 4, or 5 100-ohm unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) or shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable, complying with IEEE 802.3 10Base-T specifications. 100 Mbps Operation Category 5 100-ohm UTP or STP cable, complying with IEEE 802.3u 100Base-TX specifications. 1000 Mbps Operation Category 5 100-ohm 4-pair UTP or STP cable, complying with IEEE 802.3ab 1000Base-T specifications-Category 5e or better is recommended. See note on 1000Base-T Cable Requirements on page 38. Twinaxial copper CX4 cables Twinaxial cables complying with IEEE 802.3ak 10GBASE-CX4 specifications. Direct attach cables One-piece devices consisting of a cable with SFP+ and XFP connectors permanently attached, complying with SFF 8431 SFP+ and SFF INF 8077 specifications. Multimode fiber 62.5/125 m or 50/125 m (core/cladding) diameter, low metal content, graded index fiber-optic cables, complying with the ITU-T G.651 and ISO/IEC 793-2 Type A1b or A1a standards respectively.1 Single mode fiber 9/125 m (core/cladding) diameter, low metal content fiber-optic cables, complying with the ITU-T G.652 and ISO/IEC 793-2 Type B1 standards. 1 A mode conditioning patch cord may be needed for some Gigabit-LX installations. See "Mode Conditioning Patch Cord" on page 39 for more information. Note on 1000Base-T Cable Requirements. The Category 5 networking cables that work for 100Base-TX connections should also work for 1000Base-T, as long as all four-pairs are connected. But, for the most robust connections you should use cabling that complies with the Category 5e specifications, as described in Addendum 5 to the TIA-568-A standard (ANSI/TIA/ EIA-568-A-5). Because of the increased speed provided by 1000Base-T (Gigabit-T), network cable quality is more important than for either 10Base-T or 100Base-TX. Cabling plants being used to carry 1000Base-T networking must comply with the IEEE 802.3ab standards. In particular, the cabling must pass tests for Attenuation, Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT), and Far-End Crosstalk (FEXT). Additionally, unlike the cables for 100Base-TX, the 1000Base-T cables must pass tests for Equal-Level Far-End Crosstalk (ELFEXT) and Return Loss. When testing your cabling, be sure to include the patch cables that connect the switch and other end devices to the patch panels on your site. The patch cables are frequently overlooked when testing cable and they must also comply with the cabling standards.