HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Multicast and Routing Guide - Page 104
Configuring Option 82, dhcp-relay option, append, mgmt-vlan, replace
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 104 highlights
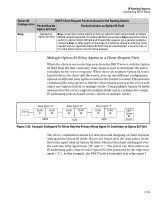
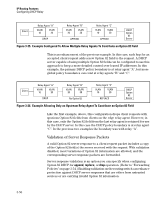
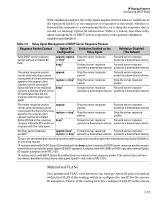
IP Routing Features Configuring DHCP Relay ID option and a DHCP client request packet is received on a multinetted VLAN, the IP address used in the Option 82 field will identify the subnet on which the packet was received instead of the IP address for the VLAN. This enables an Option 82 DHCP server to support more narrowly defined DHCP policy boundaries instead of defining the boundaries at the VLAN or whole routing switch levels. If the MAC address option (the default) is configured instead, then the routing switch MAC address will be used regardless of which subnet was the source of the client request. (The MAC address is the same for all VLANs configured on the routing switch.) Note that all request packets from DHCP clients in the different subnets in the VLAN must be able to reach any DHCP server identified by the IP Helper Address(es) configured on that VLAN. Configuring Option 82 To configure DHCP Option 82 on a routing switch, enter the dhcp-relay option 82 command. Syntax: dhcp-relay option 82 < append [validate] | replace [validate] | drop [validate] | keep > [ip | mac | mgmt-vlan] append: Configures the switch to append an Option 82 field to the client DHCP packet. If the client packet has existing Option 82 field(s) assigned by another device, the new field is appended to the existing field(s). The appended Option 82 field includes the switch Circuit ID (inbound port number*) associated with the client DHCP packet, and the switch Remote ID. The default switch remote ID is the MAC address of the switch on which the packet was received from the client. To use the incoming VLAN's IP address or the Management VLAN IP address (if configured) for the remote ID instead of the switch MAC address, use the ip or mgmt-vlan option (below). replace: Configures the switch to replace existing Option 82 field(s) in an inbound client DHCP packet with an Option 82 field for the switch. The replacement Option 82 field includes the switch circuit ID (inbound port number*) associated with the client DHCP packet, and the switch remote ID. The default switch remote ID is the MAC address of the switch on which the packet was received from the client. To use the incoming VLAN's IP address or the Management VLAN IP address (if configured) for the remote ID instead of the switch MAC address, use the ip or mgmt-vlan option (below). 3-58