HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Multicast and Routing Guide - Page 97
General DHCP Option 82 Requirements and Operation, Secondary Relay Agent, Requirements.
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 97 highlights
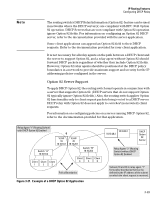
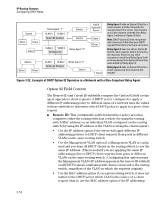
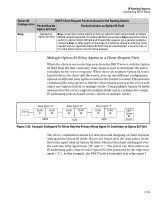
IP Routing Features Configuring DHCP Relay Secondary Relay Agent: In the path between a DHCP client and a DHCP server, any routing switch (configured to support DHCP operation) other than the primary relay agent. General DHCP Option 82 Requirements and Operation Requirements. DHCP Option 82 operation is configured at the global config level and requires the following: ■ IP routing enabled on the switch ■ DHCP-Relay Option 82 enabled (global command level) ■ routing switch access to an Option 82 DHCP server on a different subnet than the clients requesting DHCP Option 82 support ■ one IP Helper address configured on each VLAN supporting DHCP clients General DHCP-Relay Operation with Option 82. Typically, the first (primary) Option 82 relay agent to receive a client's DHCP request packet appends an Option 82 field to the packet and forwards it toward the DHCP server identified by the IP Helper address configured on the VLAN in which the client packet was received. Other, upstream relay agents used to forward the packet may append their own Option 82 fields, replace the Option 82 field(s) they find in the packet, forward the packet without adding another field, or drop the packet. (Intermediate next-hop routing switches without Option 82 capability can be used to forward-route-client request packets with Option 82 fields.) Response packets from an Option 82 server are routed back to the primary relay agent (routing switch), and include an IP addressing assignment for the requesting client and an exact copy of the Option 82 data the server received with the client request. The relay agent strips off the Option 82 data and forwards the response packet out the port indicated in the response as the Circuit ID (client access port). Under certain validation conditions described later in this section, a relay agent detecting invalid Option 82 data in a response packet may drop the packet. 3-51