HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Multicast and Routing Guide - Page 79
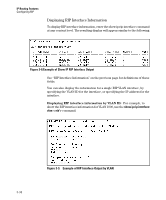
RIP Interface Information
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 79 highlights
IP Routing Features Configuring RIP ■ Default Metric - Sets the default metric for imported routes. This is the metric that will be advertised with the imported route to other RIP peers. A RIP metric is a measurement used to determine the 'best' path to network; 1 is the best, 15 is the worse, 16 is unreachable. ■ Route changes - The number of times RIP has modified the routing switch's routing table. ■ Queries - The number of RIP queries that have been received by the routing switch. ■ RIP Interface Information - RIP information on the VLAN interfaces on which RIP is enabled. • IP Address - IP address of the VLAN interface running rip. • Status - Status of RIP on the VLAN interface. • Send mode - The format of the RIP updates: RIP 1, RIP 2, or RIP 2 version 1 compatible. • Recv mode - The switch can process RIP 1, RIP 2, or RIP 2 version 1 compatible update messages. • Metric - The path "cost", a measurement used to determine the 'best' RIP route path; 1 is the best, 15 is the worse, 16 is unreachable. • Auth - RIP messages can be required to include an authentication key if enabled on the interface. ■ RIP Peer Information - RIP Peers are neighboring routers from which the routing switch has received RIP updates. • IP Address - IP address of the RIP neighbor. • Bad routes - The number of route entries which were not processed for any reason. • Last update timeticks - How many seconds have passed since we received an update from this neighbor. Syntax: show ip rip 3-33