HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Multicast and Routing Guide - Page 94
DHCP Option 82, An Option 82 DHCP server can use a relay agent's identity and client
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 94 highlights
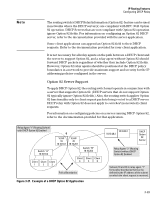
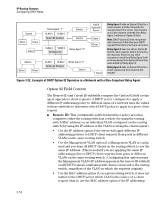
IP Routing Features Configuring DHCP Relay DHCP Option 82 Option 82 is called the Relay Agent Information option and is inserted by the DHCP relay agent when forwarding client-originated DHCP packets to a DHCP server. Servers recognizing the Relay Agent Information option may use the information to implement IP address or other parameter assignment policies. The DHCP Server echoes the option back verbatim to the relay agent in server-to-client replies, and the relay agent strips the option before forwarding the reply to the client. The "Relay Agent Information" option is organized as a single DHCP option that contains one or more "sub-options" that convey information known by the relay agent. The initial sub-options are defined for a relay agent that is co located in a public circuit access unit. These include a "circuit ID" for the incoming circuit, and a "remote ID" which provides a trusted identifier for the remote high-speed modem. The routing switch can operate as a DHCP relay agent to enable communica tion between a client and a DHCP server on a different subnet. Without Option 82, DHCP operation modifies client IP address request packets to the extent needed to forward the packets to a DHCP server. Option 82 enhances this operation by enabling the routing switch to append an Option 82 field to such client requests. This field includes two suboptions for identifying the routing switch (by MAC address or IP address) and the routing switch port the client is using to access the network. A DHCP server with Option 82 capability can read the appended field and use this data as criteria for selecting the IP addressing it will return to the client through the usual DHCP server response packet. This operation provides several advantages over DHCP without Option 82: ■ An Option 82 DHCP server can use a relay agent's identity and client source port information to administer IP addressing policies based on client and relay agent location within the network, regardless of whether the relay agent is the client's primary relay agent or a secondary agent. ■ A routing switch operating as a primary Option 82 relay agent for DHCP clients requesting an IP address can enhance network access protection by blocking attempts to use an invalid Option 82 field to imitate an authorized client, or by blocking attempts to use response packets with missing or invalid Option 82 suboptions to imitate valid response packets from an authorized DHCP server. ■ An Option 82 relay agent can also eliminate unnecessary broadcast traffic by forwarding an Option 82 DHCP server response only to the port on which the requesting client is connected, instead of broadcasting the DHCP response to all ports on the VLAN. 3-48