HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Multicast and Routing Guide - Page 74
Enabling IP RIP on a VLAN, Changing the RIP Type on a VLAN Interface
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 74 highlights
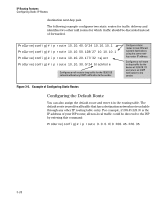
IP Routing Features Configuring RIP Note IP routing must be enabled prior to enabling RIP. The first command in the preceding sequence enables IP routing. Enabling IP RIP on a VLAN To enable RIP on all IP addresses in a VLAN, use ip rip in the VLAN context. when the command is entered without specifying any IP address, it is enabled in all configured IP addresses of the VLAN. To enable RIP on a specific IP address in a VLAN, use ip rip [< ip-addr >| all ] in the VLAN context and enter a specific IP address. If you want RIP enabled on all IP addresses, you can specify all in the command instead of a specific IP address. Changing the RIP Type on a VLAN Interface When you enable RIP on a VLAN interface, RIPv2-only is enabled by default. You can change the RIP type to one of the following on an individual VLAN interface basis: ■ Version 1 only ■ Version 2 only (the default) ■ Version 1 - or - version 2 To change the RIP type supported on a VLAN interface, enter commands such as the following: ProCurve(config)# vlan 1 ProCurve(vlan-1)# ip rip v1-only ProCurve(vlan-1)# exit ProCurve(config)# write memory Syntax: [no] ip rip < v1-only | v1-or-v2 | v2-only > Changing the Cost of Routes Learned on a VLAN Interface By default, the switch interface increases the cost of a RIP route that is learned on the interface. The switch increases the cost by adding one to the route's metric before storing the route. You can change the amount that an individual VLAN interface adds to the metric of RIP routes learned on the interface. 3-28