HP Deskjet 6980 User Guide - Macintosh - Page 22
Adapters and access points, Adapters, Access points, Wireless network examples - enable wireless
 |
UPC - 882780129580
View all HP Deskjet 6980 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
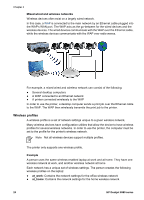
Chapter 4 802.11a is an emerging wireless networking technology that operates in the 5 GHz frequency band and offers communication speeds similar to those of 802.11g. The printer cannot communicate with 802.11a devices over a wireless connection. If you have an 802.11a wireless network, you can use an Ethernet cable to connect the printer to the network's Wireless Access Point (WAP) in order to achieve a processing speed comparable to that of the 802.11a network. If your wireless network supports 802.11g and 802.11b technology, another option is to switch the rest of the network to the lower frequency to use the printer wirelessly. To connect the printer to an Ethernet network, follow the Ethernet network installation instructions. Adapters and access points Adapters While some devices, such as the printer, have built-in Wi-Fi capability, other devices need an adapter to become Wi-Fi-enabled. AirPort® cards are available from Apple for Macintosh products. See the card documentation for installation and configuration instructions. Access points Infrastructure networks are a common variety of wireless network. An infrastructure network requires the use of a Wireless Access Point (WAP). A WAP acts as a central hub for a wireless network or as a router connecting the wireless network to another network (such as the Internet or an Ethernet network). Devices on the network communicate through the WAP. Macintosh users may use an AirPort® Base Station as a WAP. Wireless network examples To see some examples of wireless networks, see the wireless network examples page. 20 HP Deskjet 6980 series