HP Deskjet 6980 User Guide - Macintosh - Page 30
Authentication and encryption, Authentication, Definition, Types of authentication, Description - password
 |
UPC - 882780129580
View all HP Deskjet 6980 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
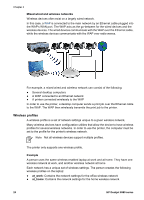
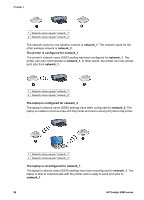
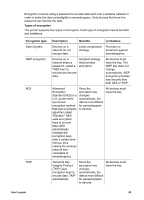
Chapter 4 Authentication and encryption Wireless security is a complex and developing topic. This page gives a brief overview of the basics involved in making a wireless network secure. In the simplest terms, wireless security involves two strategies: authentication and encryption. A wireless security method, such as WEP or WPA, involves varying levels of authentication and encryption. Authentication Definition Authentication verifies the identity of a user or device before granting access to a network, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to access network resources. In order to be authenticated and allowed to use a network, a device must supply a known password to other devices on the network. If the device cannot supply the correct password, it will not be able to use other devices on the network. Types of authentication The printer supports three types of authentication. Each type of authentication has its benefits and limitations. Authentication type Open System Shared Key WPA/PSK Description Benefits Limitations Devices on a network identify themselves with the network name (SSID) only. Least complicated strategy. Provides little protection against unauthorized users. Devices use a shared master secret to identify themselves as authorized members of the network. Convenient to use in conjunction with WEP, since a WEP key can serve as the shared authentication key. All devices must have the key. The shared key does not change automatically. Devices use a single pre-shared key (PSK) to identify themselves as authorized members of the network and to generate an encryption key. The pre-shared key and the encryption keys are not identical. Allows smaller networks to use WPA without the need for an authorization server. All devices must have the key. Encryption Definition 28 HP Deskjet 6980 series