HP Pavilion dv7-4200 Notebook PC User Guide - Windows 7 - Page 26
Setting up a WLAN, Protecting your WLAN
 |
View all HP Pavilion dv7-4200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
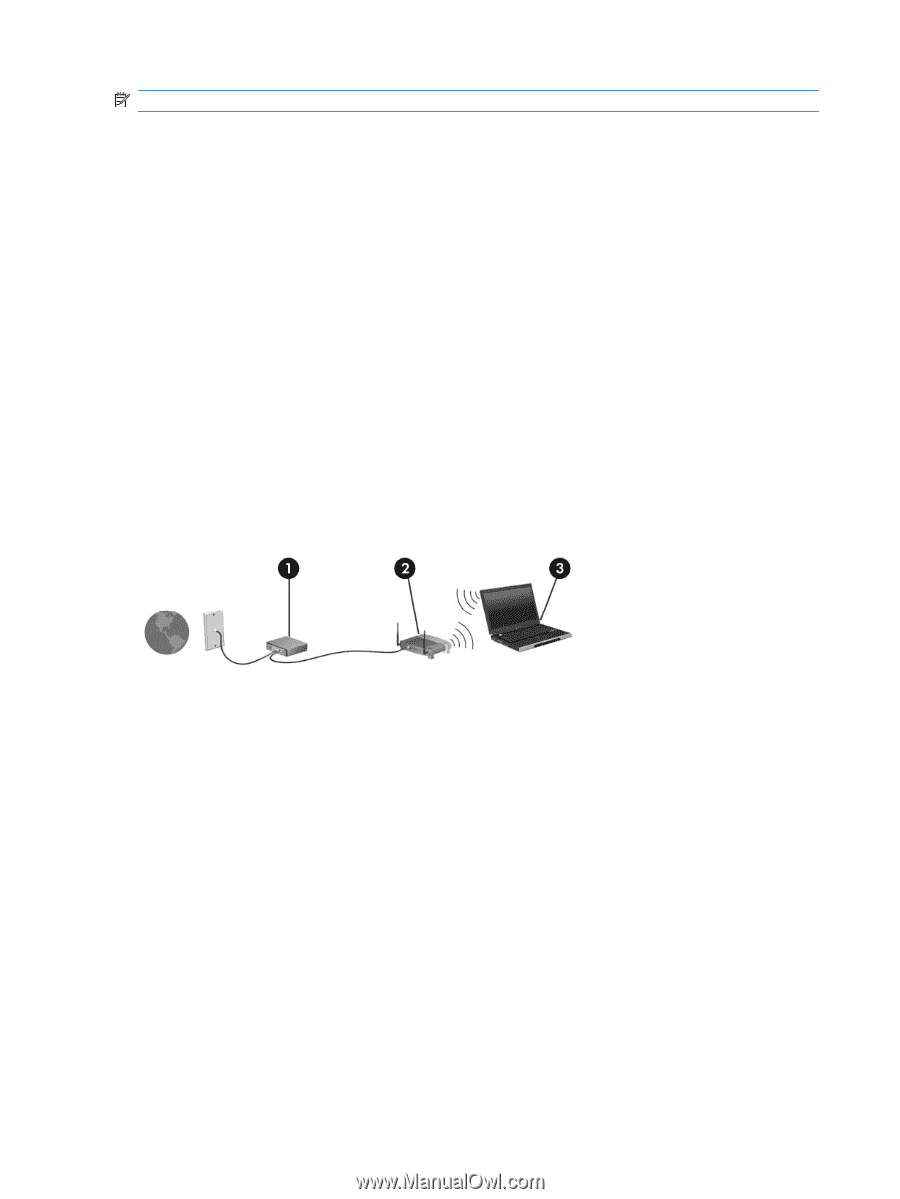
NOTE: The terms wireless router and wireless access point are often used interchangeably. ● A large-scale WLAN, such as a corporate or public WLAN, typically uses wireless access points that accommodate a large number of computers and accessories and can separate critical network functions. ● A home or small office WLAN uses a wireless router, which allows several wireless and wired computers to share an Internet connection, a printer, and files without requiring additional pieces of hardware or software. To use the WLAN device in the computer, connect to a WLAN infrastructure (provided through a service provider or a public or corporate network). Setting up a WLAN To set up a WLAN and connect to the Internet, you need: ● A broadband modem (either DSL or cable) (1) and high-speed Internet service purchased from an Internet service provider (ISP) ● A wireless router (purchased separately) (2) ● The wireless computer (3) The illustration below shows an example of a wireless network installation that is connected to the Internet. As your network grows, additional wireless and wired computers can be connected to the network to access the Internet. For help in setting up your WLAN, see the information provided by your router manufacturer or your ISP. Protecting your WLAN Because the WLAN standard was designed with only limited security capabilities-basically to foil casual eavesdropping rather than more powerful forms of attack-it is essential to understand that WLANs are vulnerable to well-known and well-documented security weaknesses. WLANs in public areas, or "hotspots," like coffee shops and airports might not provide any security. New technologies are being developed by wireless manufacturers and hotspot service providers that make the public environment more secure and anonymous. If you are concerned about the security of the computer in a hotspot, limit your network activities to noncritical e-mail and basic Internet surfing. When setting up a WLAN or access an existing WLAN, always enable security features to protect your network from unauthorized access. The common security levels are Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)Personal and Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). Because wireless radio signals travel outside the 16 Chapter 2 Wireless, local area network, and modem