HP Pavilion dv7-4200 Notebook PC User Guide - Windows 7 - Page 44
Audio, Connecting external audio devices, Checking your audio functions
 |
View all HP Pavilion dv7-4200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 44 highlights
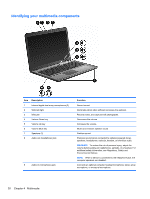
Audio The computer has a variety of audio features that allow you to: ● Play music using the computer speakers and/or connected external speakers. ● Record sound using the internal microphone or a connected external microphone. ● Download music from the Internet. ● Create multimedia presentations using audio and images. ● Transmit sound and images with instant messaging programs. ● Stream radio programs (select models only) or receiving FM radio signals. ● Create or "burn" audio CDs. Connecting external audio devices WARNING! To reduce the risk of personal injury, adjust the volume before putting on headphones, earbuds, or a headset. For additional safety information, see the Regulatory, Safety and Environmental Notices. To connect external devices such as external speakers, headphone, or a microphone, see the information provided with the device. For best results: ● Be sure that the device cable is securely connected to the correct jack on the computer. Cable connectors are normally color-coded to match the corresponding jacks on the computer. ● Be sure that you install all drivers required by the external device. NOTE: A driver is a required program that acts like a translator between the device and the programs that use the device. Checking your audio functions To check the system sound on the computer: 1. Select Start >Control Panel. 2. Click Hardware and Sound. 3. Click Sound. 4. When the Sound window appears, click the Sounds tab. 5. Under Program Events, select any sound event, such as a beep or alarm. 6. Click the Test button. You should hear sound through the speakers or through connected headphones. To check the record functions: 1. Select Start >All Programs >Accessories >Sound Recorder. 2. Click Start Recording and speak into the microphone. For best results when recording, speak directly into the microphone and record sound in a setting free of background noise. 34 Chapter 4 Multimedia