HP Scitex FB500 HP Scitex FB500 and FB700 Printer Series - User Guide - Page 33
Use white ink, Introduction, White ink option overview, Types of white ink printing - capabilities
 |
View all HP Scitex FB500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 33 highlights
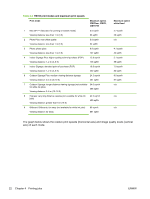
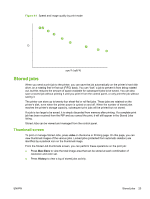
5 Use white ink Introduction With the white ink option available from HP, you can replace the light magenta and light cyan inks with white ink, resulting in four colors of ink plus white ink. This enables you to print with white ink using various techniques. Printing with white ink may require special preparation of the image to be printed or special setup in the RIP. Refer to the documentation provided with the application software and RIP for step-by-step procedures. White ink option overview White ink printing is available as an option that can be delivered with a new printer or as a field upgrade to an existing printer. If the option is delivered with a new printer, it is installed with the new printer. In the case of a field upgrade, the option is designed to be installed either by a service technician or by the customer operator. The white ink option consists of two parts (see instructions that accompany the kit for detailed instructions): ● White ink option upgrade - a one-time process that upgrades the printer to a white-ink capable printer ● White ink conversion - replaces the existing light cyan and light magenta inks in the printer with white ink. Refer to the White Ink Upgrade Kit Installation Instructions, HP part number CQ114-90006, included in the white ink upgrade accessory kit, for detailed instructions for the upgrade and conversion. Types of white ink printing Many different design effects can be achieved with white ink that would not be possible otherwise, especially when printing on dark, colored, metallic, or clear media. There are three basic design techniques for printing with white ink: ● Under-fill - a solid rectangle (or irregular shape) of printed white ink that is cured, then a color image is printed on top of it. When used on a non-white, transparent, or reflective surface, this can provide better color saturation or allow colors that are similar to the media color to be visible. ● Over-fill - a color image is printed and cured, a solid rectangle (or irregular shape) of white ink is printed on top of it. This is most often printed on clear media to create a sign that is viewed on a light box (for example, a shopping mall map, airport advertisement, or bus stop signage). When viewed from the opposite side of the media on which it was printed, the image must be reversed (mirrored) in the RIP or application software before printing. ● Spot color - any white shape (including text) that is cured with and in the same plane as the rest of the artwork, rather than in a separate plane or layer. In conventional (analog) offset or screen printing, this might be called a "knockout," because none of the colors are overprinted. NOTE: When printing a CMYK or CMYKcm image without a white under-fill on non-white media, color saturation may be reduced, depending on the color of the media used. ENWW Introduction 27