Intel E2160 Design Guide - Page 38
Intel® Quiet System Technology (Intel® QST), 6.1 Intel® QST Algorithm, Intel, QST Algorithm
 |
UPC - 735858199216
View all Intel E2160 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
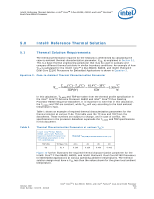
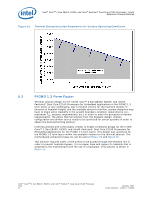
Intel® CoreTM 2 Duo E6400, E4300, and Intel® Pentium® Dual-Core E2160 Processor-Intel® Quiet System Technology (Intel® QST) 6.0 Note: 6.1 Intel® Quiet System Technology (Intel® QST) In the Intel® 965 Express Chipset family, a new control algorithm for fan speed control is being introduced. It is composed of a Manageability Engine (ME) in the Graphics Memory Controller Hub (GMCH) which executes the Intel® Quiet System Technology (Intel® QST) algorithm and the ICH8 containing the sensor bus and fan control circuits. The ME provides integrated fan speed control in lieu of the mechanisms available in a SIO or a stand-alone ASIC. The Intel QST is time based as compared to the linear or state control used by the current generation of FSC devices. A short discussion of Intel QST will follow along with thermal solution design recommendations. For a complete discussion of programming the Intel QST in the ME, consult the Intel® Quiet System Technology (Intel® QST) Configuration and Tuning Manual. Fan speed control algorithms and Intel QST in particular rely on a thermal solution being compliant to the processor thermal profile. It is unlikely that any fan speed control algorithm can compensate for a non-compliant thermal solution. See Chapter 5.0 and Chapter 6.0 for thermal solution requirements that should be met before evaluating or configuring a system with Intel QST. Intel® QST Algorithm The objective of Intel QST is to minimize the system acoustics by more closely controlling the thermal sensors to the corresponding processor or chipset device TCONTROL value. This is achieved by the use of a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control algorithm and a Fan Output Weighting Matrix. The PID algorithm takes into account the difference between the current temperature and the target (TCONTROL), the rate of change and direction of change to minimize the required fan speed change. The Fan Output Weighting Matrix uses the effects of each fan on a thermal sensor to minimize the required fan speed changes Figure 13 shows in a very simple manner how Intel QST works. Refer to the Intel® Quiet System Technology (Intel® QST) Configuration and Tuning Manual for details of the inputs and response. Intel® CoreTM 2 Duo E6400, E4300, and Intel® Pentium® Dual-Core E2160 Processor TDG 38 October 2007 Order Number:315279 -003US