Lantronix XPress-DR XPress-DR / XPress-DR-IAP - User Guide - Page 19
Serial Interface, 3.1 Packing Algorithm, 3.2 IP Address, 3.3 Port Number
 |
View all Lantronix XPress-DR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
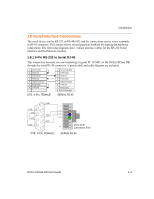
Introduction 1.3.1 Packing Algorithm The two available packet algorithms (which define how and when packets are sent to the network) are software selectable. The standard algorithm is optimized for applications where DSTni-XPress DR is used in a local environment, allowing for very small delays for single characters while trying to keep the packet count low. The alternate packing algorithm minimizes the packet count on the network and is especially useful for applications in routed Wide Area Networks. Various parameters can be set in this mode to economize the serial data stream. 1.3.2 IP Address Every active device connected to the TCP/IP network must have a unique IP address. This IP address is used to reference a specific device, for example, to build a connection to DSTniXPress DR's serial port. See IP Addresses on page 10-1 for a complete description of IP Addressing. 1.3.3 Port Number A destination IP address and a port number define every TCP connection and every UDP datagram. A port number is necessary to address an application or a channel on a network host. The port number can be compared to an extension on a PBX system. A Telnet application (login to a host with an ASCII terminal) is commonly assigned TCP port number 23. More than one Telnet connection can be established to one host using the Telnet port; however, the other peer IP address/port number combinations must be different. In the DSTni-XPress DR, a port number can be configured on the channel (port). The DSTniXPress DR uses this port number for outgoing messages and incoming connections, or UDP datagrams, which are addressed to its port number. Port 9999 (decimal) is used for remote configuration. 1.4 Serial Interface DSTni-XPress DR has a single serial port that can be accessed by an RJ-45 connector or screw block terminals. Both connectors support RS232 and RS485/422. By setting the switch located on the face of the DSTni-XPress DR, RS232 or RS485/422 can be selected. Note: DSTni-XPress DR is a single serial port device, meaning that only the RJ-45 or the screw terminals can be used at a time. In the configuration menu, Channel 1 refers to either one of the ports being used. DSTni-XPress DR User Guide 1-5