Netgear WNA1000 WNA1000 User Manual - Page 46
Optimizing Your Network Bandwidth, connection speeds. - windows 10
 |
View all Netgear WNA1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
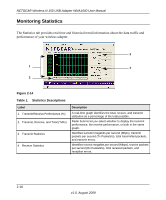
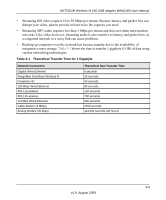
NETGEAR Wireless-N 150 USB Adapter WNA1000 User Manual Avoid windows unless communicating between buildings. Place wireless devices away from various electromagnetic noise sources, especially those in the 2400-2500 MHz frequency band. Common noise-creating sources are: - Computers and fax machines (no closer than 1 foot) - Copying machines, elevators, and cell phones (no closer than 6 feet) - Microwave ovens (no closer than 10 feet) • Choose your settings. - Use a scanning utility to determine what other wireless networks are operating nearby, and choose an unused channel. - Turn off SSID Broadcast, and change the default SSID. Other nearby devices might automatically try to connect to your network several times a second, which can cause significant performance reduction. Optimizing Your Network Bandwidth The speed of network connections depends on the type of equipment that you use. Try to use highspeed technologies for network connections with the heaviest traffic to avoid lower-speed bottlenecks in the path. Figure 3-1 on page 3-3 shows a home network that includes many different connection speeds. In this network, the two PCs with gigabit (1000 Mbps) Ethernet adapters have a gigabit connection through the router to the storage server. With a high-speed router this connection allows for extremely fast backups or quick access to large files on the server. The PC connected through a pair of Powerline HD adapters is limited to the 200 Mbps speed of the Powerline HD connection. Although any of the links in this example would be sufficient for high-traffic applications such as streaming HD video, the use of older devices such as 10 Mbps Ethernet or 802.11b wireless would create a significant bottleneck. 3-2 v1.0, August 2009