Netgear WNA1000 WNA1000 User Manual - Page 49
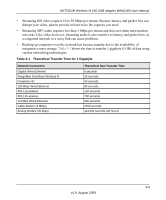
Table 3-1., Theoretical Transfer Time for 1 Gigabyte
 |
View all Netgear WNA1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
NETGEAR Wireless-N 150 USB Adapter WNA1000 User Manual • Streaming HD video requires 10 to 30 Mbps per stream. Because latency and packet loss can disrupt your video, plan to provide at least twice the capacity you need. • Streaming MP3 audio requires less than 1 Mbps per stream and does not strain most modern networks. Like video, however, streaming audio is also sensitive to latency and packet loss, so a congested network or a noisy link can cause problems. • Backing up computers over the network has become popular due to the availability of inexpensive mass storage. Table 3-1 shows the time to transfer 1 gigabyte (1 GB) of data using various networking technologies. Table 3-1. Theoretical Transfer Time for 1 Gigabyte Network Connection Gigabit Wired Ethernet RangeMax Dual Band Wireless-N Powerline HD 100 Mbps Wired Ethernet 802.11g wireless 802.11b wireless 10 Mbps Wired Ethernet Cable Modem (3 Mbps) Analog Modem (56 kbps) Theoretical Raw Transfer Time 8 seconds 26 seconds 40 seconds 80 seconds 150 seconds 700 seconds 800 seconds 2700 seconds 144,000 seconds (40 hours) 3-5 v1.0, August 2009