TRENDnet TEW-828DRU User's Guide - Page 51
Virtual Private Networking (VPN), Creating a Virtual Private Network
 |
View all TRENDnet TEW-828DRU manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 51 highlights
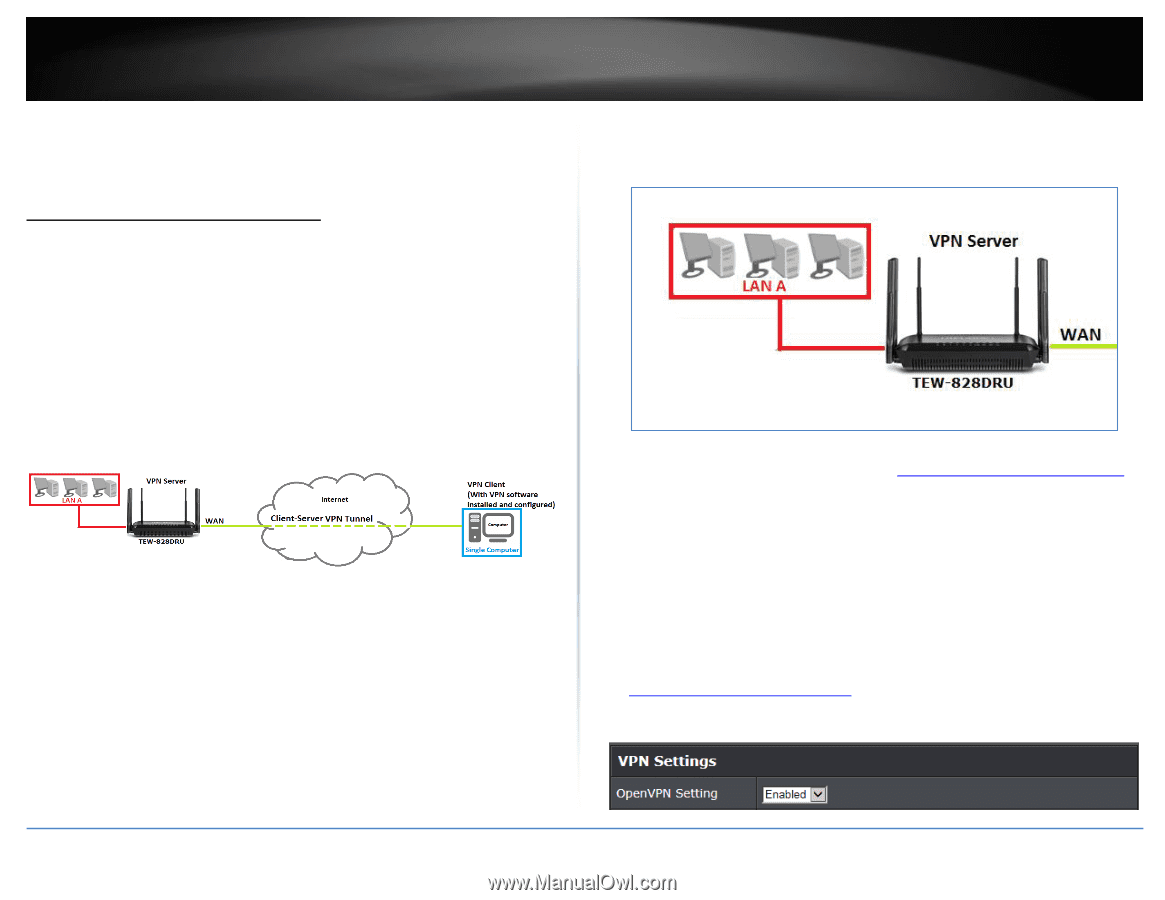
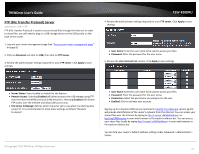
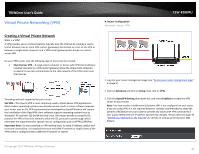
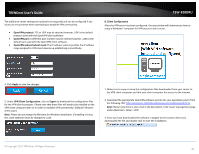
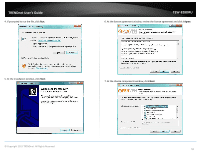
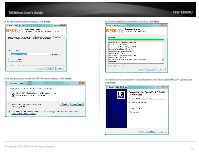
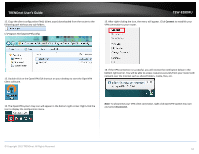
TRENDnet User's Guide Virtual Private Networking (VPN) Creating a Virtual Private Network What is a VPN? A VPN provides secure communications typically over the Internet by creating a secure tunnel between two or more VPN routers (gateways) also known as a site-to-site VPN or between a single client computer and a VPN router (gateway) also known as a clientserver VPN. On your VPN router, only the following type of tunnel can be created: Client-Server VPN - A single client computer or device with VPN client software installed connects to a VPN router (gateway) allow the single client computer or device to securely communicate to the LAN network of the VPN router over the Internet. Tunneling methods supported by your router: SSL VPN - This type of VPN is most commonly used in Client-Server VPN applications. Most modern operating systems may already include a built-in client software however, your router uses an SSL VPN implementation developed by OpenVPN which will require the installation of the OpenVPN client software supports operating systems such as Windows® XP and later (32-bit/64-bit) and Linux. One major benefit to using the SSL protocol for VPN is that most networks allow the SSL protocol to passthrough which eliminates the requirement for special rules or configuration such as PPTP/L2TP/IPsec. Important Note: For any tunneling or VPN method used, to avoid IP address conflict and to ensure connectivity, it is required that each end (LAN IP network or single client) of the VPN tunnel is configured with a different IP network or subnet. A. Router Configuration Advanced > Setup > VPN TEW-828DRU 1. Log into your router management page (see "Access your router management page" on page 9). 2. Click on Advanced and click on Setup, then click on VPN. 3. Click the OpenVPN Setting drop-down list, and select Enabled to enable the VPN server on your router. Note: You may receive a notification if Dynamic DNS is not configured on your router. If you are using VPN, it is not required however, strongly recommended to setup the Dynamic DNS feature on your router to prevent any issues with VPN connectivity if your public (WAN) Internet IP address dynamically changes. Please reference page 34 "Identify your Network on the Internet" for details on setting up the Dynamic DNS feature. © Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved. 48