Cisco SGE2000 Reference Guide - Page 23
Understanding Stack Resiliency, Understanding Advanced Stacking, Unit IDs, Stack Master - sge2000p manual
 |
View all Cisco SGE2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
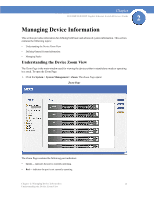
Chapter SGE2000/SGE2000P Gigabit Ethernet Switch Reference Guide 2 3. Power the units on. After a short interval, they will become stack members, but will have automatically-assigned Unit IDs. Assign each such unit its desired Unit ID (using the Stack Management Interface through the console port, by Telnet, or by using the graphical user interface (GUI). 4. Reset the units to make this assignment permanent. NOTE: We recommended that if you manually assign a Unit ID to one unit, you manually assign Unit IDs to all units. Using a mix of both system-assigned and manuallyassigned IDs in your network can impact system performance. The unit that is assigned the Unit ID 1 is the Stack Master, and its front panel "MST" LED lights green. The unit assigned the Unit ID 2 is the Backup Master. Understanding Stack Resiliency Stacks can be configured in ring or chain topologies. We recommend configuring the stack in ring topology, due to the high resiliency in case of unit failure or stacking links failure. Additionally, if a redundant power supply is present, we recommend connecting the Stack Master and Backup Master units to the redundant power supply. Understanding Advanced Stacking To understand advanced stacking, you must understand Unit IDs and how they are allocated, and the stack unit startup process. Unit IDs Each unit in a stack has an assigned unique Unit ID number. The following sections describe the Unit IDs and their characteristics. Stack Master The unit assigned the Unit ID number 1 serves as the Stack Master. All other units are stack members. The Stack Master provides a single point of control, configuration and management for the entire stack, and stores the configuration for all stack members. (Members do not store any configuration information.) Stack Backup Master The unit assigned the Unit ID number 2 is a special stack member that serves as the stack Backup Master. A stack Backup Master assumes the role of Stack Master for the remaining stack members if the stack Master fails or is disconnected. Chapter 2: Managing Device Information 15 Understanding Stack Resiliency