Craftsman 10872 Operation Manual - Page 12
Ripping or Rip Cut, lengthof, workpiece, End or Edge, enters
 |
View all Craftsman 10872 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 12 highlights
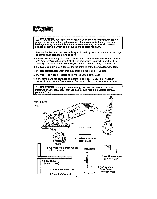
Compound Miter Cut A compound miter cut is a cut made using a miter angle and a bevel angle at the same time. Cross Cut A cutting or shaping operation made across the grain of the work piece° Bevel Cut A cutting operation made with the blade at any angie other than 90 ° to the miter table. Dado Cut A non-through cut wllich produces a square-sided (requires special blade). notch or trough in the workpiece Chamfer Cut A cut removing a wedge from a block of wood so the end (or part of the end) is angled at other than 90 ° . Ripping or Rip Cut A cutting operation along the length of the workpiece,or cutting along the grain. Freehand Cut Performing a cut without using a fence, miter gauge, fixture, work clamp, or other proper device to keep the workpiece from twisting or moving during the cut Through Sawing Any cutting operation where the blade extends completely through the thickness of the workpiece. Non-Through Cuts Any cutting operation where the b_ade does not extend completely through the thickness of the workpiece, like a dado cut. Leading End (or Edge) The end (edge) of the workpiece that the blade enters first Kerr The material removed by the blade in a through cut or the siot produced by the blade in a non-through or partial cuL Kickback A hazard that can occur when the blade binds or stalls, throwing the saw back toward operator_ Workptece or Material The item on which the cutting operation is being done The surfaces of a workpiece are commonly referred to as faces, ends and edges. Gum A sticky, sap-based residue from wood products. Resin A sticky, sap-based substance that has hardened. 12