HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches IPv6 Configuration Guide - Page 100
Address Lifetimes, Preferred Lifetime, Valid Lifetime, Sources of IPv6 Address Lifetimes
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 100 highlights
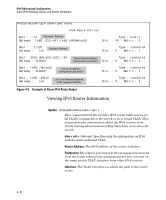
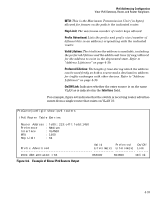
IPv6 Addressing Configuration Address Lifetimes Address Lifetimes Every configured IPv6 unicast and anycast address has a lifetime setting that determines how long the address can be used before it must be refreshed or replaced. Some addresses are set as "permanent" and do not expire. Others have both a "preferred" and a "valid" lifetime that specify the duration of their use and availability. Preferred Lifetime This is the length of time during which the address can be used freely as both a source and a destination address for traffic exchanges with other devices. This time span is equal to or less than the valid lifetime also assigned to the address. If this time expires without the address being refreshed, the address becomes deprecated and should be replaced with a new, preferred address. In the deprecated state, an address can continue to be used as a destination for existing communication exchanges, but is not used for new exchanges or as a source for traffic sent from the interface. A new, preferred address and its deprecated counterpart will both appear in the show ipv6 vlan < vid > output as long as the deprecated address is within its valid lifetime. Valid Lifetime This is the total time the address is available, and is equal to or greater than the preferred lifetime. The valid lifetime enables communication to continue for transactions that began before the address became deprecated. However, in this timeframe, the address should no longer be used for new communica tions. If this time expires without the deprecated address being refreshed, the address becomes invalid and may be assigned to another interface. Sources of IPv6 Address Lifetimes Manually configured addresses have permanent lifetimes. The prefixes received from router advertisements for global unicast addresses include finite valid and preferred lifetime assignments. Refer to "Unicast Address Prefixes" on page 3-11. 4-34