HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches IPv6 Configuration Guide - Page 143
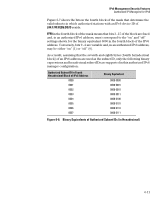
FF:FEB6:D37D, Binary Equivalents of Authorized Subnet IDs in Hexadecimal
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 143 highlights
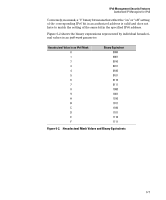
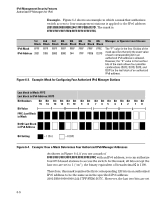
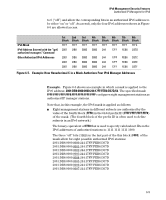
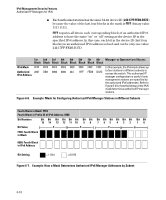
IPv6 Management Security Features Authorized IP Managers for IPv6 Figure 6-7 shows the bits in the fourth block of the mask that determine the valid subnets in which authorized stations with an IPv6 device ID of 244:17FF:FEB6:D37D reside. FFF8 in the fourth block of the mask means that bits 3 - 15 of the block are fixed and, in an authorized IPv6 address, must correspond to the "on" and "off" settings shown for the binary equivalent 0000 in the fourth block of the IPv6 address. Conversely, bits 0 - 2 are variable and, in an authorized IPv6 address, may be either "on" (1) or "off" (0). As a result, assuming that the seventh and eighth bytes (fourth hexadecimal block) of an IPv6 address are used as the subnet ID, only the following binary expressions and hexadecimal subnet IDs are supported in this authorized IPv6 manager configuration: Authorized Subnet ID in Fourth Hexadecimal Block of IPv6 Address 0000 0001 0002 0003 0004 0005 0006 0007 Binary Equivalent 0000 0000 0000 0001 0000 0010 0000 0011 0000 0100 0000 0101 0000 0110 0000 0111 Figure 6-8. Binary Equivalents of Authorized Subnet IDs (in Hexadecimal) 6-11