HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches IPv6 Configuration Guide - Page 65
IPv6 Address Deprecation, Preferred and Valid Address Lifetimes
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 65 highlights
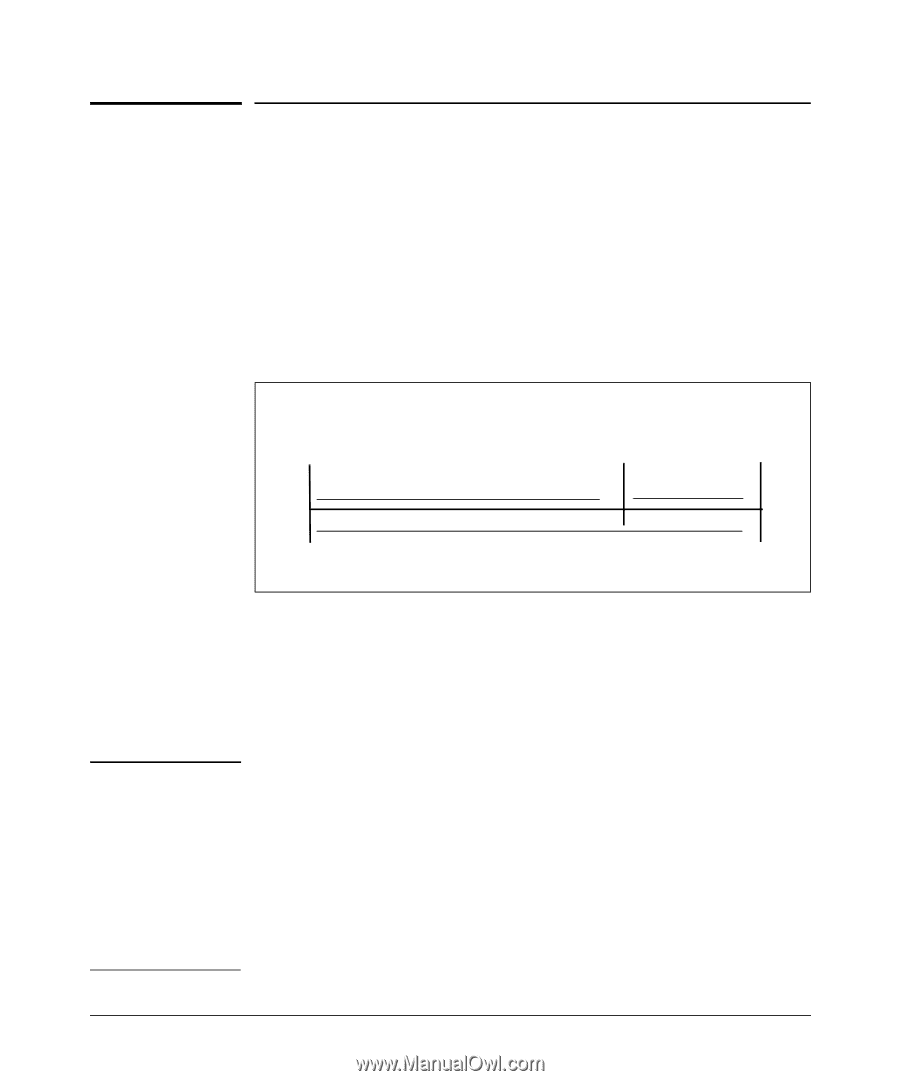
Notes IPv6 Addressing IPv6 Address Deprecation IPv6 Address Deprecation Preferred and Valid Address Lifetimes Autoconfigured IPv6 global unicast addresses acquire their valid and preferred lifetime assignments from router advertisements. A valid lifetime is the time period during which an address is allowed to remain available and usable on an interface. A preferred lifetime is the length of time an address is intended for full use on an interface, and must be less than or equal to the address's valid lifetime. Address "Preferred" End of Preferred Lifetime Address "Deprecated" Address Acquired Valid Lifetime Address Removed Figure 3-1. Valid and Preferred Lifetimes When the preferred lifetime expires, the address becomes deprecated, meaning that the address should no longer be used as a source address (except for existing exchanges that began before the timeout occurred), but can still be used as a destination. When the timeout arrives for the valid lifetime, the address becomes unusable. Preferred and valid lifetimes on a VLAN interface are determined by the router advertisements received on the interface. These values are not affected by the lease time assigned to an address by a DHCPv6 server. That is, lease expiration on a DHCPv6-assigned address terminates use of the address, regardless of the status of the RA-assigned lifetime, and router-assigned lifetime expiration of a leased address terminates the switch's use of the address. (The routerassigned lifetime can be extended by receipt of a new router advertisement.) Statically configured IPv6 addresses are regarded as permanent addresses, and do not expire. 3-25