HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches IPv6 Configuration Guide - Page 96
Default IPv6 Router, Router Redirection, RFC 2461: Neighbor Discovery for IP Version 6
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 96 highlights
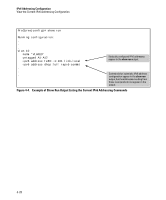
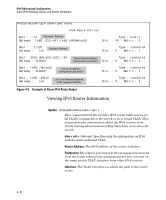
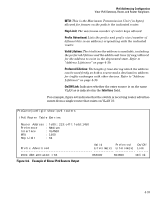
IPv6 Addressing Configuration Router Access and Default Router Selection Note If the switch does not receive a router advertisement after sending the router solicitations, as described above, then no further router solicitations are sent on that VLAN unless a new IPv6 setting is configured, IPv6 on the VLAN is disabled, then re-enabled, or the VLAN itself is disconnected, then recon nected. Default IPv6 Router If IPv6 is enabled on a VLAN where there is at least one accessible IPv6 router, the switch selects a default IPv6 router. (Refer to "Enabling Autoconfiguration of a Global Unicast Address and a Default Router Identity on a VLAN" on page 4-7.) ■ If the switch receives router advertisements (RAs) from a single IPv6 router on the same VLAN or subnet, the switch configures a global unicast address and selects the advertising router as the default IPv6 router. ■ If multiple IPv6 routers on a VLAN send RAs advertising the same network, the switch configures one global unicast address and selects one router as the default router, based on the router's relative reachability, using factors such as router priority and route cost. ■ If multiple IPv6 routers on a VLAN send RAs advertising different subnets, the switch configures a corresponding global unicast address for each RA and selects one of the routers as the default IPv6 router, based on route cost. When multiple RAs are received on a VLAN, the switch uses the router priority and route cost information included in the RAs to identify the default router for the VLAN. Router Redirection With multiple routers on a VLAN, if the default (first-hop) router for an IPv6 enabled VLAN on the switch determines that there is a better first-hop router for reaching a given, remote destination, the default router can redirect the switch to use that other router as the default router. For further information on routing IPv6 traffic, refer to the documentation provided for the IPv6 router. For related information: ■ RFC 2461: "Neighbor Discovery for IP Version 6" 4-30