HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch High Availability Configuration Guide - Page 54
VF tracking, Protocols and standards, Configuring IPv4 VRRP, IPv4 VRRP configuration task list
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 54 highlights
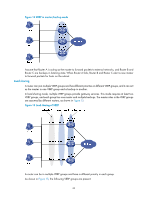
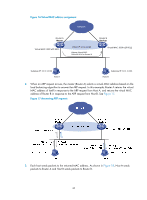
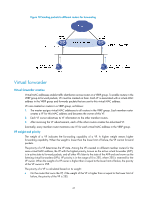
• Redirect timer-Before this timer expires, the master still uses the virtual MAC address corresponding to the failed AVF to respond to ARP/ND requests from hosts, and the VF owner can share traffic load if the VF owner resumes normal operation within this time. When this timer expires, the master stops using the virtual MAC address corresponding to the failed AVF to respond to ARP/ND requests from hosts. • Timeout timer-The duration after which the new AVF takes over responsibilities of the failed VF owner. Before this timer expires, all routers in the VRRP group keep the VFs that correspond to the failed AVF, and the new AVF forwards packets destined for the virtual MAC address of the failed AVF. When this timer expires, all routers in the VRRP group remove the VFs that correspond to the failed AVF, including the new AVF. Packets destined for the virtual MAC address of the failed AVF are not forwarded any longer. VF tracking An AVF forwards packets destined for the MAC address of the AVF. If the upstream link of the AVF fails but no LVF takes over the AVF role, the hosts on the subnet that use the MAC address of the AVF as their gateway MAC address cannot access the external network. The VF tracking function can solve this problem. You can use NQA or BFD to monitor the upstream link state of the VF owner, and establish the collaboration between the VFs and NQA or BFD through the tracking function. When the upstream link fails, the state of the track entry changes to Negative, and the weights of the VFs (including the AVF) on the router decrease by a specified value. The corresponding LVF with a higher priority on another router becomes the AVF and forwards packets. Protocols and standards • RFC 3768, Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) • RFC 5798, Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) Version 3 for IPv4 and IPv6 Configuring IPv4 VRRP IPv4 VRRP configuration task list Tasks at a glance (Required.) Specifying an IPv4 VRRP operating mode (Optional.) Specifying the IPv4 VRRP version (Required.) Creating a VRRP group and assigning a virtual IP address (Optional.) Configuring the router priority, preemptive mode, and tracking function (Optional.) Configuring IPv4 VRRP packet attributes (Optional.) Configuring VF tracking (Optional.) Disabling an IPv4 VRRP group Remarks N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A This configuration applies to only VRRP load balancing mode. N/A 49