HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch High Availability Configuration Guide - Page 55
Specifying an IPv4 VRRP operating mode, Specifying the IPv4 VRRP version
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 55 highlights
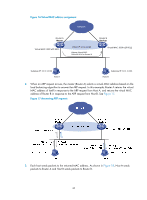
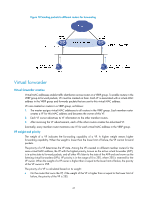
Specifying an IPv4 VRRP operating mode A VRRP group can operate in either of the following modes: • Standard mode-Only the master can forward packets. • Load balancing mode-All members that have an AVF can forward packets. After an IPv4 VRRP operating mode is configured on a router, all IPv4 VRRP groups on the router operate in the specified operating mode. To specify an IPv4 VRRP operating mode: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Specify an IPv4 VRRP operating mode. Command system-view • Specify the standard mode: undo vrrp mode • Specify the load balancing mode: vrrp mode load-balance Remarks N/A Use one of the commands. By default, VRRP operates in standard mode. Specifying the IPv4 VRRP version The VRRP version on all routers in an IPv4 VRRP group must be the same. To specify the version of IPv4 VRRP: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter interface view. 3. Specify the version of VRRP. Command system-view interface interface-type interface-number vrrp version version-number Remarks N/A N/A By default, VRRPv3 is used. Creating a VRRP group and assigning a virtual IP address A VRRP group can operate properly after you create it and assign at least one virtual IP address to it. You can configure multiple virtual IP addresses for the VRRP group on an interface that connects to multiple subnets for router backup on different subnets. Configuration guidelines • In VRRP load balancing mode, the device supports a maximum of MaxVRNum/N VRRP groups. MaxVRNum refers to the maximum number of VRRP groups supported by the device in VRRP standard mode, and N refers to the number of devices in the VRRP group. • When VRRP is operating in standard mode, the virtual IP address of a VRRP group can be either an unused IP address on the subnet where the VRRP group resides or the IP address of an interface on a router in the VRRP group. • In load balancing mode, the virtual IP address of a VRRP group can be any unassigned IP address of the subnet where the VRRP group resides, rather than the IP address of any interface in the VRRP group. No IP address owner can exist in a VRRP group. 50