HP Integrity Superdome SX1000 SmartSetup Scripting Toolkit Deployment Guide: H - Page 49
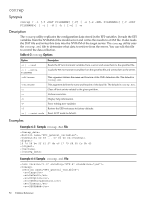
CLMChecking, Synopsis, Description, Examples, Table 6-2, Options
 |
View all HP Integrity Superdome SX1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
Target on ID #2 Device is a Hard disk Enclosure # : 1 Slot # : 2 Target ID : 2 State : Ready (RDY) Size (in MB)/(in sectors) : 57231/117210240 Manufacturer : ATA Model Number : FUJITSU MHT2060B Firmware Revision : 034E Serial No : NR0LT5625AAG Drive Type : SATA Enclosure information Enclosure# : 1 Logical ID : 50060b00:00c13846 Numslots : 8 StartSlot : 1 Start TargetID : 0 Start Bus : 0 CLMChecking Synopsis CLMChecking -p | -v | -h Description Perform memory optimization in cellular systems. On cellular systems the available system memory can be accessed using two different approaches: Interleaved memory Meaning that the average memory latency is constant for all processes in the system. Non-interleaved memory Meaning that lower memory latency is provided for processes running in the same cell as the memory. For each cell, it is possible to determine the amount of memory that should not be interleaved. The non-interleaved memory is known as cell local memory (CLM) or global non-interleaved (GNI) memory. The amount of cell local memory can affect directly the system overall performance. If running Windows, better performance can be obtained with maximum CLM. Table 6-2 CLMChecking Options Options -p -v | --version -h | --help Description Print the CLM values of the cells in the partition. Print the CLMChecking version. Print help. Examples SSTK-v.3.2# ./CLMChecking Partition #0: CLM Cell 0 = 7 CLM Cell 2 = 7 Partition #1: CLM Cell 1 = 7 CLM Cell 3 = 7 CLMChecking 49