Netgear WNHD3004 WNHD3004 User Manual - Page 39
Using the DHCP Server, Optimizing Wireless Performance
 |
View all Netgear WNHD3004 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
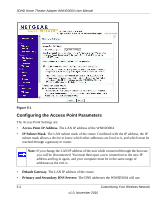
3DHD Home Theater Adapter WNHD3004 User Manual Using the DHCP Server Warning: If two DHCP servers in a network are configured to give out conflicting addresses, the network will crash an none of the devices on the network will be able to use it until one of the DHCP servers is removed from the network. Be sure to avoid DHCP server conflicts with the DHCP server in your router by having them manage different address ranges in the same subnet. For most applications, the default DHCP and TCP/IP settings of the WNHD3004 are satisfactory. Click the link to the online document "TCP/IP Networking Basics" in Appendix B for an explanation of DHCP and information about how to assign IP addresses for your network. By default, the DHCP server of WNHD3004 is disabled. You can enable it to assign IP, DNS server, and default gateway addresses to all computers connected to the LAN. The assigned default gateway address is the LAN address of the router. The router assigns IP addresses to the attached computers from a pool of addresses specified in this screen. Each pool address is tested before it is assigned to avoid duplicate addresses on the LAN. Specify the pool of IP addresses to be assigned by setting the starting IP address and ending IP address. These addresses should be part of the same IP address subnet as the router's LAN IP address. Optimizing Wireless Performance The speed and operating distance or range of your wireless connection can vary significantly based on the physical placement of the wireless router. You should choose a location for your router that will maximize the network speed. Note: Failure to follow these guidelines can result in significant performance degradation or inability to wirelessly connect to the router. For complete range and performance specifications, click the link to the online document "Wireless Networking Basics" in Appendix B. The following list describes how to optimize wireless router performance. Customizing Your Wireless Network 5-3 v1.0, November 2010