Netgear XM128 QIG - Quick Install Guide - Page 36
Understanding AT Commands
 |
View all Netgear XM128 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 36 highlights
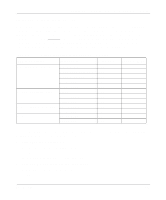
Reference Guide for the Model XM128 ISDN Digital Modem The setup procedure for the Model XM128 modem needs to be done only once because the settings are stored in the nonvolatile RAM of the modem and turning the power off does not erase the information. The only time you have to reconfigure your line is when you perform a hardware reset or when you change options on your ISDN line. Note: If you perform a hardware reset and have to reenter the SPID number(s) and switch type again, it is easier if you write down or store all the relevant information so it can be easily retrieved. Table 4-1 shows a list of example terminal programs for different operating platforms. For instructions on how to use a terminal program, refer to the instructions that came with the program. Table 4-1. Terminal programs Operating system Windows 95 Windows 3.x UNIX DOS Macintosh Program Hyper Terminal Terminal Procomm Plus for Windows Qmodem for Windows Minicomm PC Plus Qmodem Z-Term Communicate Lite Understanding AT Commands AT commands configure and control the Model XM128 modem through a terminal program. Command statements are usually sent to the modem from the computer keyboard. Command statements must be written in a specific form in order for the Model XM128 modem to recognize them. A command statement begins with the letters AT or at. It is then followed by one or more commands and the Enter key. AT commands can be issued only when the Model XM128 modem is in command or offline mode. After the Model XM128 modem has established a connection with the remote device, it goes into online mode, and the characters sent from your computer (through the modem) are transmitted to the remote device. 4-2 Configuration