Netgear XM128 QIG - Quick Install Guide - Page 72
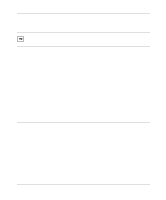
The command AT&ZO?
 |
View all Netgear XM128 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 72 highlights
Reference Guide for the Model XM128 ISDN Digital Modem The number-subaddress string s is defined as: s = [[Yn][Nn]own-number][/[[Zn]own-subaddress]/] Yn specifies the type of number: • Y0 for unknown (default if Yn is omitted) • Y1 for international number • Y2 for national number • Y3 for network specific number • Y4 for subscriber number Nn is the identifier of the numbering plan: • N0 for unknown (default if Nn is omitted) • N1 for ISDN numbering plan (Rec. E.164) (default for Australia if Nn is omitted) • N3 for data numbering plan (Rec. X.121) • N4 for telex numbering plan (Rec. F.69) • N8 for national standard numbering plan • N9 for private numbering plan Zn specifies the subaddress type: • Z0 for NSAP (Rec. X.213) with AFI=0x50, IA5 characters (default if Zn is omitted) • Z2 for user specified, IA5 characters The command AT&ZOx=// removes the number/subaddress assignment. The number and subaddress assigned by AT&ZOx=s, if any, can be used for calling-party number and calling-party subaddress information elements, respectively, while dialing. The default settings of the phone number and subaddress of all the types of calls are UNASSIGNED, meaning the setup message sent by the Model XM128 modem contains neither calling-party number nor calling-party subaddress information elements. The command AT&ZO? can be used to browse the current settings of the known numbers and subaddresses. 7-4 Advanced ISDN