Netgear XM128 QIG - Quick Install Guide - Page 87
Modem Upgrade
 |
View all Netgear XM128 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 87 highlights
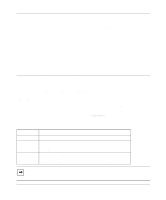
Chapter 9 Modem Upgrade This chapter describes how to upgrade flash electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM) firmware on your Model XM128 ISDN Digital Modem. Upgrading with Flash EPROM Your Model XM128 modem employs a flash EEPROM that lets you conveniently download updated firmware and program the modem with new features and enhanced functions. If you are using Windows 95 or Windows NT, use the NETGEAR Internet Configuration Manager to upgrade the firmware. For other operating systems, use a terminal program that supports the X-modem Protocol. Obtain the new firmware from the NETGEAR bulletin board system (BBS), WWW, or FTP site. Refer to Customer Support on page -iii. The firmware is distributed in the ONETd.vvv file, where the extension vvv denotes the version of this firmware. Table 9-1 lists the definitions for the d modifier in the file name. Table 9-1. Modifier G E A Definitions for the d modifier Definition German national ISDN (1TR6) European ISDN (DSS1) European ISDN is also used in most other countries including Asian countries. American ISDN (AT&T 5ESS, Northern Telecom DMS-100, or National ISDN-1) The active D channel protocol can be chosen by an AT command. Note: The American firmware version supports both the S/T interface and U interface models. During power-on test, it checks the hardware configuration and follows the initialization procedures of the specific interface. Modem Upgrade 9-1