Panasonic KX-P3696 Operating Instructions - Page 71
Panasonic KX-P3696 Manual
 |
View all Panasonic KX-P3696 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 71 highlights
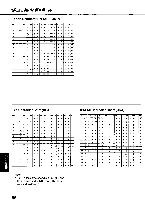
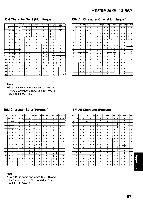
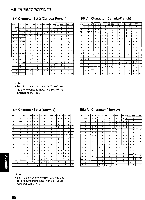
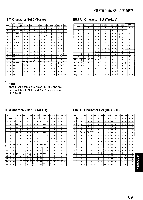
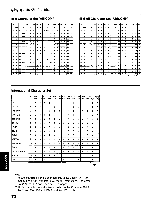
a 0 0 ASCII: "ASCII" is an acronym for "American Standard Code for Information Interchange". In ASCII, each character has a unique code. BASIC: BASIC is a commonly used microcomputer programming language. Baud (baud rate): Baud is a unit of data transmission speed between computer devices. Can be, but not necessarily, equal to bits per second. Bidirectional printing: Processing speed is increased by bidirectional printing. That is, the printer prints right-to-left as well as in the normal left-to-right manner. Binary: Binary is a numbering system using the two digits of zero (0) and one (1). Bit: Bit is an abbreviation for "binary digit (0-1)", and is the smallest unit of information used by a printer or computer. Bit-image graphics: Graphics which are created through a series of dots printed in vertical columns. Buffer: Buffer is an area of memory which stores data temporarily. Byte: Byte is the unit of information used by a printer or computer. One byte is equivalent to eight (8) bits. Character set: Character set is the set of characters, numbers, and symbols available for printing. Code page: The computer system stores characters and numbers as a numerical data. The code page is a table which is used to change them into the numerical data. Control codes: Control codes are commands from the computer to the printer that are non-printable characters. They are used to control printer functions. cpi: "cpi" is an abbreviation for "characters per inch", and means the maximum number of characters printed in one horizontal inch. cpl: "cpl" is an abbreviation for "characters per line", and means the maximum number of characters printed on one line. cps: "cps" is an abbreviation for "characters per second", and means the number of characters printed in one second. CR (Carriage Return): "CR" is a control code that returns the printhead to the left margin. Decimal (Dec.): Decimal is a numbering system composed of 10 digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9. Default: Default has two meanings: one indicates the previously set conditions or settings executed when the power is turned on, reset or initialized; and the other indicates the original settings when shipped from the factory. Dots per inch (DPI): A measure of resolution used for monitors and printers. Download character: Download character is a character which the user can design. Draft: Draft is one of two print qualities available on this -o printer. Draft mode uses a minimum number of m dots per character to maximize printing speed. Emulation: Emulation means to operate like another printer. This printer can emulate the Epson FX-1170 or the IBM Proprinter IIIXL. 71