TRENDnet TEW-740APBO Users Guide - Page 27
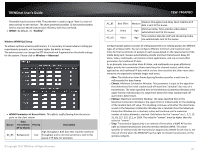
Wireless WMM QoS Setup, Wireless -> Advanced, WMM Parameters of Access Point, Aifsn, CWmin, CWmax
 |
View all TRENDnet TEW-740APBO manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 27 highlights
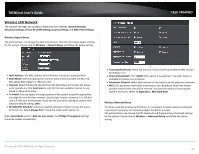
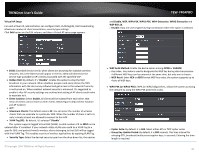
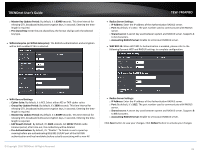
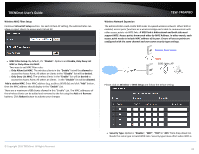
TRENDnet User's Guide Preamble Synchronization field. The preamble is used to signal "here is a train of data coming" to the receiver. The short preamble provides 72-bit Synchronization field to improve WLAN transmission efficiency with less overhead. WMM: By default, it's "Enabled". Wireless WMM QoS Setup To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower. The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced WMM Parameters of Access Point : This affects traffic flowing from the access point to the client station Data Queue Transmitted Priority AP to Clients Description AC_BK Background. High throughput. Bulk data that requires maximum Low throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this queue (FTP data, for example). © Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved. TEW-740APBO AC_BE AC_VI AC_VO Best Effort Video Voice Medium Medium throughput and delay. data is sent to this queue Most traditional IP High Minimum delay. Time-sensitive video data is automatically sent to this queue High Time-sensitive data like VoIP and streaming media are automatically sent to this queue Configuring QoS options consists of setting parameters on existing queues for different types of wireless traffic. You can configure different minimum and maximum wait times for the transmission of packets in each queue based on the requirements of the media being sent. Queues automatically provide minimum transmission delay for Voice, Video, multimedia, and mission critical applications, and rely on best-effort parameters for traditional IP data. As an Example, time-sensitive Voice & Video, and multimedia are given effectively higher priority for transmission (lower wait times for channel access), while other applications and traditional IP data which are less time-sensitive but often more dataintensive are expected to tolerate longer wait times. o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in milliseconds) for data frames o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the algorithm that determines the initial random back-off wait time ("window") for retry of a transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random back-off wait time is determined. o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling of the random back-off value. This doubling continues until either the data frame is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum number of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the value for "cwmin". o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) for AP; that is, the interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the wireless network. 27