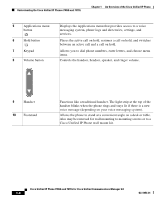
Cisco CP-7911G Administration Guide - Page 25
Cisco Unified IP Phones use the RTP
 |
View all Cisco CP-7911G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
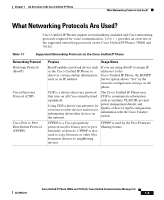
Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco Unified IP Phone What Networking Protocols Are Used? Table 1-1 Supported Networking Protocols on the Cisco Unified IP Phone (continued) Networking Protocol Internet Protocol (IP) Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP) Purpose Usage Notes IP is a messaging protocol that addresses and sends packets across the network. To communicate using IP, network devices must have an assigned IP address, subnet, and gateway. IP addresses, subnets, and gateways identifications are automatically assigned if you are using the Cisco Unified IP Phone with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). If you are not using DHCP, you must manually assign these properties to each phone locally. RTP is a standard protocol for transporting real-time data, such as interactive voice and video, over data networks. Cisco Unified IP Phones use the RTP protocol to send and receive real-time voice traffic from other phones and gateways. RTCP works with RTP to provide QoS data (such as jitter, latency, and round trip delay) on RTP streams. RTCP is disabled by default, but you can enable it on a per phone basis using Cisco Unified Communications Manager. For more information, see the "Network Configuration" section on page 4-34. SRTP is available in addition to RTP. SRTP adds security by encrypting media streams during data transport. For SRTP to work, the phone or phones being called must also support SRTP or else those phones cannot decrypt the secure media stream. OL11954-01 Cisco Unified IP Phone 7906G and 7911G for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 6.0 1-7