D-Link DGS-3208TG User Guide - Page 73
Clear Address Table, SNMP Manager Configuration
 |
UPC - 790069239366
View all D-Link DGS-3208TG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 73 highlights
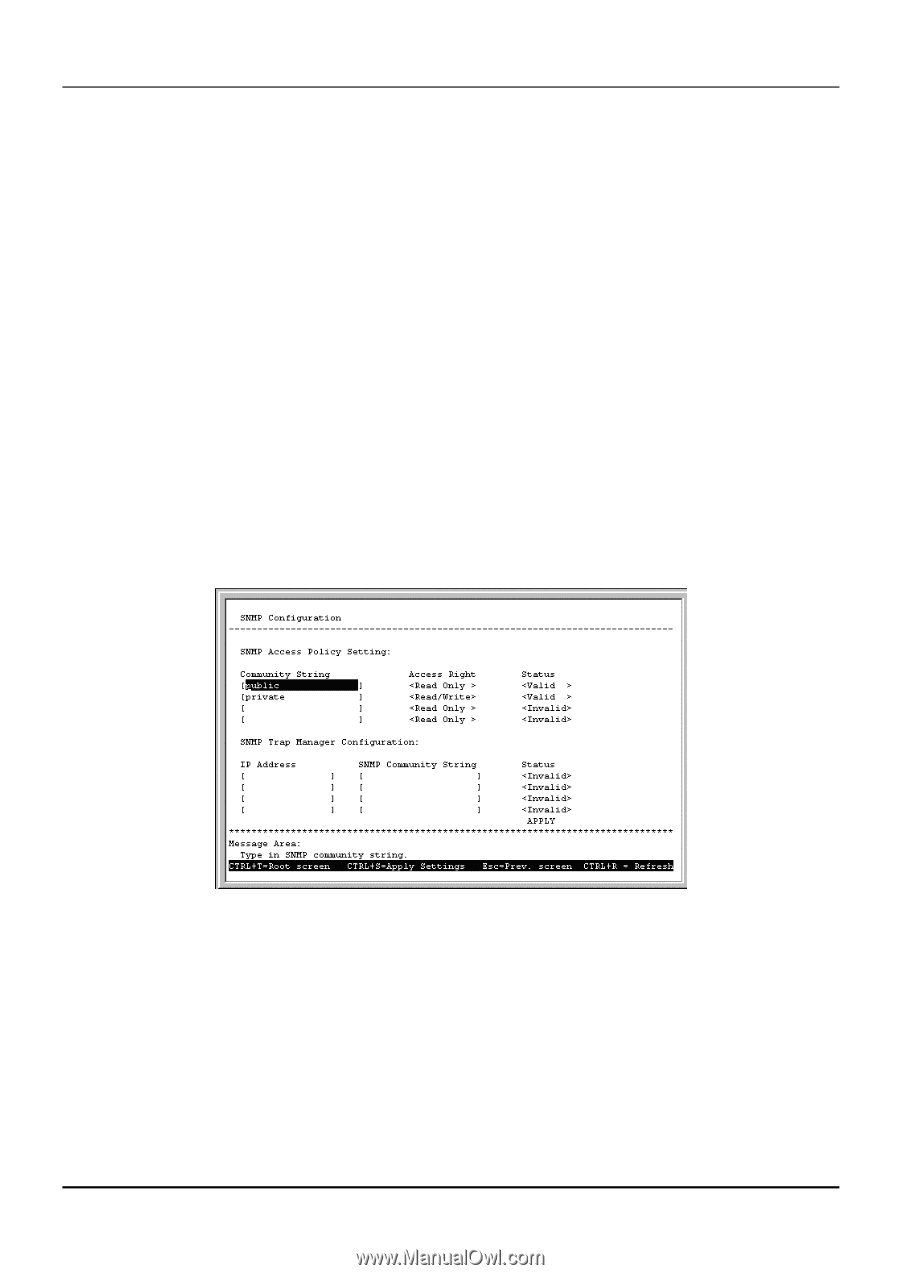
Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Guide Clear Address Table Choose Clear Address Table from the Utilities menu (under System Utilities on the main menu) to clear the entire Address Table (also known as the Filtering and Forwarding table). SNMP Manager Configuration The Switch sends out SNMP traps to network management stations whenever certain exceptional events occur, such as when the Switch is turned on or when a system reset occurs. The Switch allows traps to be routed to up to four different network management hosts. For a detailed list of Trap Types used for this Switch, see the Traps section of Chapter 5, "Switch Management Concepts." SNMP (version 1) implements a rudimentary form of security by requiring that each request include a community name. A community name is an arbitrary string of characters used as a "password" to control access to the Switch. If the Switch receives a request with a community name it does not recognize, it will trigger an authentication trap. The SNMP allows up to four different community names to be defined. The community name public is defined by default; you can change this name in addition to adding others. You will need to coordinate these names with the community name settings you use in your network management system. Choose SNMP Manager Configuration from the main menu to access the following screen: Figure 6-50. SNMP Configuration screen The following parameters can be set: ♦ Community String/SNMP Community String Determines the community name to be included in the trap request. ♦ Access Right Allows each community to be separately set to either Read Only or Read/Write. ♦ Status Determines whether this community name entry is Valid or Invalid. An entry can be deleted by changing its status to Invalid. ♦ IP Address The IP address of the network management station to receive the trap. 61