HP StorageWorks 8/80 Brocade Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator's Guide - Page 124
Traffic class mapping, Unicast traffic
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 124 highlights
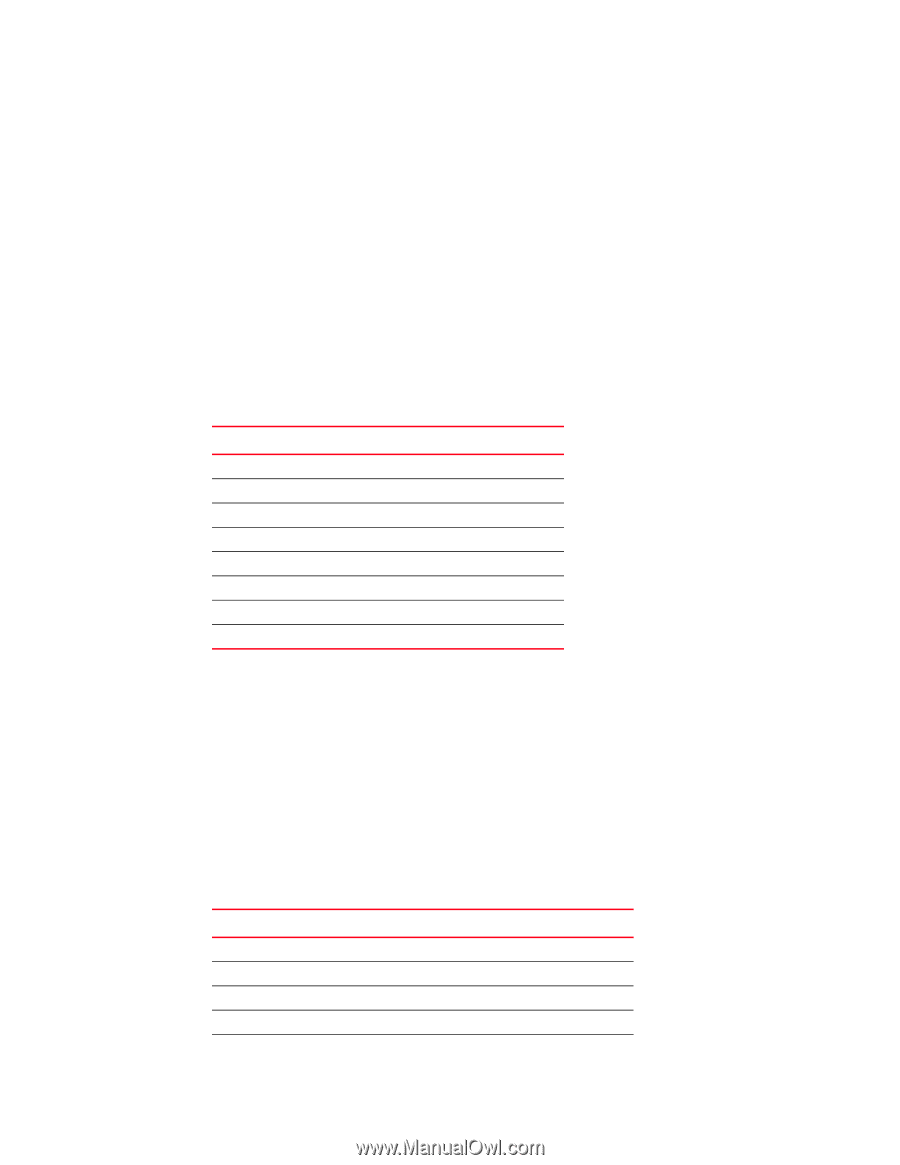
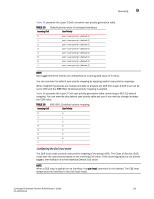
9 Queueing Traffic class mapping The Brocade 8000 supports eight unicast traffic classes for isolation and to control servicing for different priorities of application data. Traffic classes are numbered from 0 through 7, with higher values designating higher priority. The traffic class mapping stage provides some flexibility in queue selection: • The mapping may be many-to-one, such as mapping one byte user priority (256 values) to eight traffic classes. • There may be a non-linear ordering between the user priorities and traffic classes. Unicast traffic Table 17 presents the Layer 2 default traffic class mapping supported for a COS-based user priority to conform to 802.1Q default mapping. TABLE 17 Default user priority for unicast traffic class mapping User priority Traffic class 0 1 1 0 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 You are allowed to override these default traffic class mappings per port. Once the traffic class mapping has been resolved it is applied consistently across any queueing incurred on the ingress and the egress ports. Multicast traffic The Brocade 8000 supports four multicast traffic classes for isolation and to control servicing for different priorities of application data. Traffic classes are numbered from 0 through 3, with higher values designating higher priority. The traffic class mapping stage provides some flexibility in queue selection. Table 18 presents the Layer 2 default traffic class mapping supported for a COS-based user priority to conform to 802.1Q default mapping. TABLE 18 Default user priority for multicast traffic class mapping User Priority Traffic class 0 0 1 0 2 1 3 1 4 2 104 Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator's Guide 53-1001346-01