HP StorageWorks 8/80 Brocade Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator's Guide - Page 127
Changing the Tail Drop threshold,
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 127 highlights
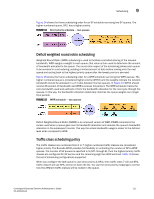
Congestion control 9 consume the full buffer memory. Thresholds can also be used to bound the maximum queueing delay for each traffic class. Additionally if the sum of the thresholds for a port is set below 100 percent of the buffer memory, then you can also ensure that a single port does not monopolize the entire shared memory pool. FIGURE 13 Queue depth The tail drop algorithm can be extended to support per priority drop thresholds. When the ingress port CoS queue depth breaches a threshold, then any frame arriving with the associated priority value will be dropped. Figure 13 shows how you can utilize this feature to ensure lower priority traffic cannot totally consume the full buffer memory. Thresholds can also be used to bound the maximum queueing delay for each traffic class. Additionally if the sum of the thresholds for a port is set below 100 percent of the buffer memory then you can also ensure that a single CoS does not monopolize the entire shared memory pool allocated to the port. Changing the Tail Drop threshold Perform the following steps from Privileged EXEC mode to change the Tail Drop threshold. 1. Enter global configuration mode. switch#configure terminal 2. Change the Tail Drop threshold for each multicast traffic class. In this example, 1000pkt is used. switch(config)#qos rcv-queue multicast threshold 1000 1000 1000 1000 Example of increasing multicast frame expansion Tail Drop Threshold to 1000pkt for each multicast Traffic Class. switch:admin>cmsh switch>enable switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. switch(config)#qos rcv-queue multicast threshold 1000 1000 1000 1000 switch(config)#end 3. Enter the copy command to save the running-config file to the startup-config file. switch#copy running-config startup-config Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator's Guide 107 53-1001346-01