HP t505 Administrator Guide 5 - Page 153
root > security, root > sshd, root > time
 |
View all HP t505 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 153 highlights
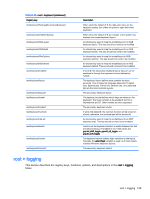
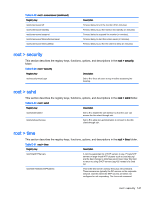
Table E-28 root > screensaver (continued) Registry key root/screensaver/off root/screensaver/standby root/screensaver/suspend root/screensaver/timeoutScreensaver root/screensaver/timeoutSleep Description Timeout delay to turn the monitor off (in minutes). Timeout delay to put the monitor into standby (in minutes). Timeout delay to suspend the monitor (in minutes). Timeout delay to start the screen saver (in minutes). Timeout delay to put the thin client to sleep (in minutes). root > security This section describes the registry keys, functions, options, and descriptions in the root > security folder. Table E-29 root > security Registry key Description root/security/mustLogin Set to 1 to force all users to log in before accessing the desktop. root > sshd This section describes the registry keys, functions, options, and descriptions in the root > sshd folder. Table E-30 root > sshd Registry key Description root/sshd/enabled Set to 1 to enable the ssh daemon so that the user can access the thin client through ssh. root/sshd/userAccess Set to 1 to allow non-adminstrators to connect to the thin client through ssh. root > time This section describes the registry keys, functions, options, and descriptions in the root > time folder. Table E-31 root > time Registry key Description root/time/NTPServers A comma-separated list of NTP servers to use. Private NTP servers or large virtual NTP clusters such as 'pool.ntp.org' are the best choices to minimize server load. Clear this field to return to using DHCP servers (tag 42) instead of a fixed list. root/time/TimeServerIPAddress This is the time server used by the Linux net command. These servers are typically the DC servers on the corporate network. Use this when the NTP servers are either not configured or not responding. The Linux net command root > security 141