Kyocera FS 1020D FS-1020D Operation Guide Rev 1.4 - Page 56
Postcards, Table 4-1, Thick Paper, Colored Paper, Preprinted Paper, Recycled Paper
 |
View all Kyocera FS 1020D manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 56 highlights
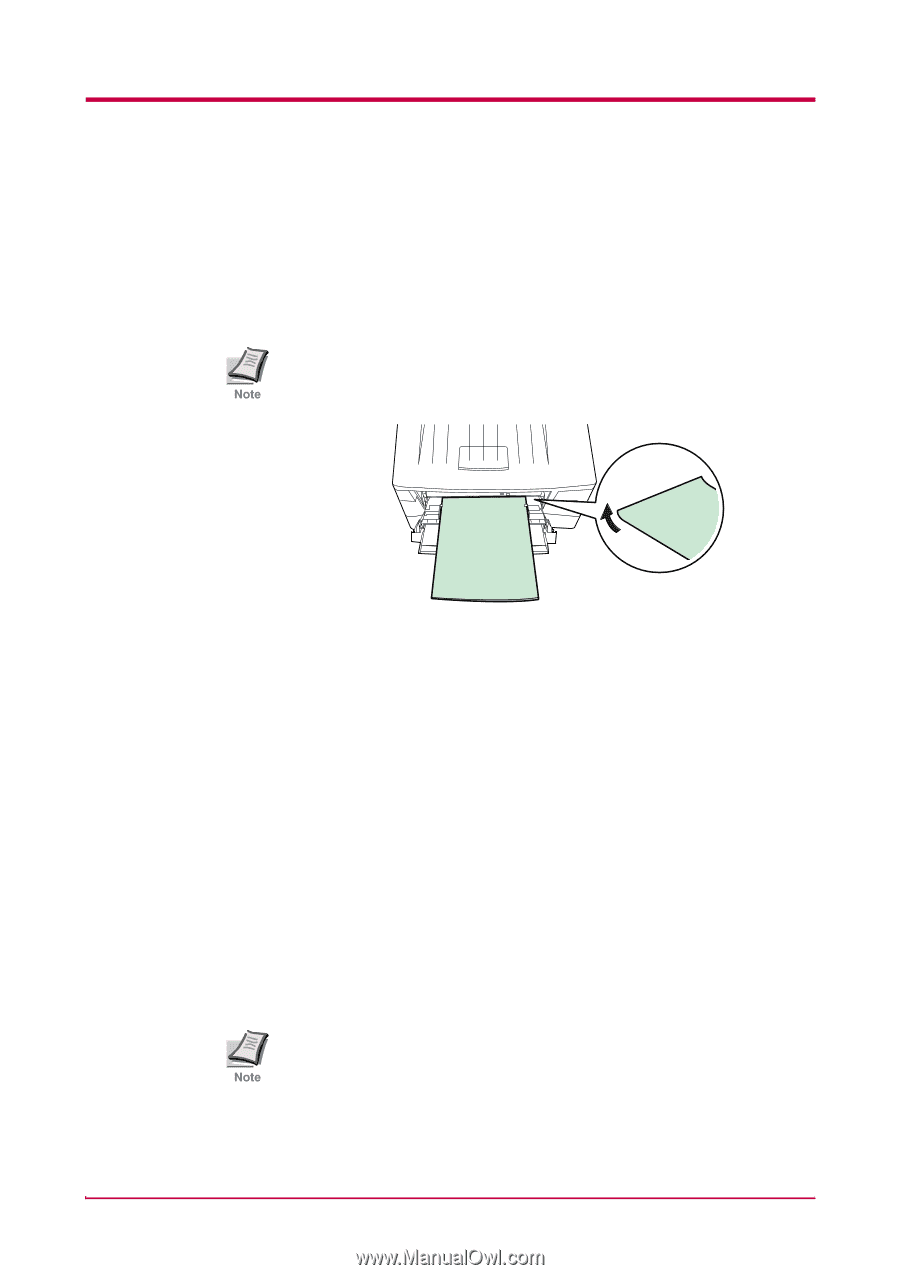
Special Paper Thick Paper Fan the stack of paper and align the edges before loading them in the MP tray. Some types of paper have rough edges on the back (those are created when the paper is cut). In this case, put the paper on a flat place and rub the edges once or twice with, for example, a ruler to smooth them in the same way as described in Postcards on page 4-9. Feeding rough edged paper may cause paper jams. If the paper jams even after you smooth it out in such a way, set the paper in the MP tray with the leading edge raised up a few millimeters as shown Note in the illustration. Figure 4-4 Colored Paper Colored paper should satisfy the same conditions as white bond paper, listed in Table 4-1 on page 4-2. In addition, the pigments used in the paper must be able to withstand the heat of fusing during the printing process (up to 200°C or 392°F). Preprinted Paper Preprinted paper should have a bond paper base. The preprinted ink must be able to withstand the heat of fusing during the printing process, and must not be affected by silicone oil. Do not use paper with any kind of surface treatment, such as the type of paper commonly used for calendars. Recycled Paper Select recycled paper that meets the same specifications as the white bond paper (see Table 4-1 on page 4-2.) except whiteness. Before purchasing recycled paper, test a sample on the printer and check that the printing quality is satisfactory. Note 4-10